Struts2拦截器的概念和Spring Mvc拦截器一样。
1.Struts2拦截器是在访问某个Action或Action的某个方法,字段之前或之后实施拦截,并且Struts2拦截器是可插拔的,拦截器是AOP的一种实现.
2.拦截器栈(Interceptor Stack)。Struts2拦截器栈就是将拦截器按一定的顺序联结成一条链。在访问被拦截的方法或字段时,Struts2拦截器链中的拦截器就会按其之前定义的顺序被调用。
使用拦截器的第一步:
自定义我的权限拦截器CheckPrivilegeInterceptor,这个拦截器继承自AbstractInterceptor这个抽象类,当然你可以实现Interceptor这个接口。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.AbstractInterceptor;import com.shizongger.oa.domain.User;public class CheckPrivilegeInterceptor extends AbstractInterceptor { @Override public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { System.out.println("---拦截器未拦截之前---"); String result = invocation.invoke(); System.out.println("---拦截器拦截之后---"); return result; }} |
自定义的拦截器要覆盖AbstractInterceptor抽象类的抽象方法intercept()方法,该方法是对所有的action进行拦截,String类型的返回值是我们将要返回的视图,如果要放行我们要拦截的action地址,那么代码如上所示。
使用拦截器的第二步:
配置struts的配置文件,主要是配置自定义的拦截器和配置拦截器栈。在struts.xml配置文件的package元素节点下添加以下配置:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<!-- 配置拦截器 --> <interceptors> <!-- 声明拦截器 --> <interceptor name="checkPrivilege" class="com.shizongger.oa.util.CheckPrivilegeInterceptor"></interceptor> <!-- 重新定义默认的拦截器栈 --> <interceptor-stack name="defaultStack"> <interceptor-ref name="checkPrivilege"></interceptor-ref> <interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"></interceptor-ref> </interceptor-stack> </interceptors> |
启动我的Tomcat服务器,当我在浏览器输入我的action地址时,都会被该拦截器的intercept拦截,默认是放行的,如果返回空字符串则因找不到对应的视图而报错。
登录和权限拦截
拦截器在Web开发中应用场景最多的地方就是登录验证和权限验证了。对于那些未登录系统的用户,一般我们都把他所有的请求打回到登录页面。而对于那些已经登录系统的用户,如果你不具有相应的权限,那么将无法访问我们的url。
首先在监听器中最一些系统做一些监听任务。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener { Log log = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass()); @Autowired private PrivilegeService privilegeService; @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) { log.debug("---销毁监听器---"); } @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { ServletContext sc = sce.getServletContext(); ApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc); PrivilegeService privilegeService = (PrivilegeService) ac.getBean("privilegeServiceImpl"); List<Privilege> topPrivilegeList = privilegeService.findTopList(); //将权限list放到比application作用域还大的ServletContext sc.setAttribute("topPrivilegeList", topPrivilegeList); // 准备数据:allPrivilegeUrls Collection<String> allPrivilegeUrls = privilegeService.getAllPrivilegeUrls(); sc.setAttribute("allPrivilegeUrls", allPrivilegeUrls); }} |
监听器的任务是从Web容器中获得Spring的容器ApplicationContext,再从ApplicationContext中获得权限服务类privilegeService,这个service主要作用有两点,其一是获得有多的顶级权限列表;其二是获得所以权限列表。将这两者放入到application里边。
接下来就可以在我们的拦截器中写登录拦截的逻辑代码了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { //获取信息,从session中取出当前登录用户 User user = (User) ActionContext.getContext().getSession().get("user"); String nameSpace = invocation.getProxy().getNamespace(); String actionName = invocation.getProxy().getActionName(); //对应的权限地址 String privilegeUrl = nameSpace + actionName; //如果未登录 if(user == null) { //如果是去登录的页面和登录请求,就放行 if("/user_login".equals(privilegeUrl)) { return invocation.invoke(); //否则跳转到登录页面 } else { return "loginUI"; } } else { //如果已经登录则判断是否有权限 if(user.hasPrivilegeByUrl(privilegeUrl)) { return invocation.invoke(); } else { return "noPrivilegeError"; } }} |
处理的逻辑是,如果未登录,则判断是不是要去登录,如果用户正在登录则放行,其他请求都要跳转到loginUI登录页面。如果已经登录,则判断正在登录的用户是否具有相对应的权限。而判断是否具有权限的方法在我的user.java里面。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
|
/** * 用户实体 * @author shizongger * @date 2017/03/24 */public class User { private Log log = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass()); private Long id; private String loginName; private String password; private String name; private String gender; private String phoneNumber; private String email; private String description; private Department department; private Set<Role> roles; //getter/settter方法 /** * 判断用户是否用该权限 * @param privilegename 权限名称 * @return */ public boolean hasPrivilegeByName(String privilegeName) { log.debug("权限名称:" + privilegeName); //从本用户中取出所有角色 for(Role role : roles) { //从角色遍历出所有权限 Set<Privilege> privilegeList = role.getPrivileges(); for(Privilege privilege : privilegeList) { if(privilegeName.equals(privilege.getName())) { log.debug(privilegeName + "---有权限---"); return true; } } } log.debug(privilegeName + "---没有权限---"); return false; } /** * 判断本用户是否有指定URL的权限 * * @param privUrl * @return */ public boolean hasPrivilegeByUrl(String privUrl) { // 超级管理有所有的权限 if (isAdmin()) { return true; } // >> 去掉后面的参数 int pos = privUrl.indexOf("?"); if (pos > -1) { privUrl = privUrl.substring(0, pos); } // >> 去掉UI后缀 if (privUrl.endsWith("UI")) { privUrl = privUrl.substring(0, privUrl.length() - 2); } // 如果本URL不需要控制,则登录用户就可以使用 Collection<String> allPrivilegeUrls = (Collection<String>) ActionContext.getContext().getApplication().get("allPrivilegeUrls"); if (!allPrivilegeUrls.contains(privUrl)) { return true; } else { // 普通用户要判断是否含有这个权限 for (Role role : roles) { for (Privilege priv : role.getPrivileges()) { if (privUrl.equals(priv.getUrl())) { return true; } } } return false; } } /** * 判断本用户是否是超级管理员 * * @return */ public boolean isAdmin() { return "admin".equals(loginName); }} |
hasPrivilegeByUrl()方法为根据url判断用户是否具有权限的代码逻辑,此逻辑分为三部分。其一,如果登录的用户是超级管理员admin,则不用验证权限,该用户具有所有的权限。其二,如果登录的用户基本功能部分不用验证,需要验证的功能才需要验证。基础功能模块比如首页,退出,登录页面等都不要再验证。
权限的service实现类如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@Servicepublic class PrivilegeServiceImpl extends DaoSupportImpl<Privilege> implements PrivilegeService { @Override @Transactional public List<Privilege> findTopList() { List<Privilege> topPrivletList = this.getSession() .createQuery("FROM Privilege p WHERE p.parent IS NULL") .list(); return topPrivletList; } @Override @Transactional public Collection<String> getAllPrivilegeUrls() { return getSession().createQuery(// "SELECT DISTINCT p.url FROM Privilege p WHERE p.url IS NOT NULL")// .list(); }} |
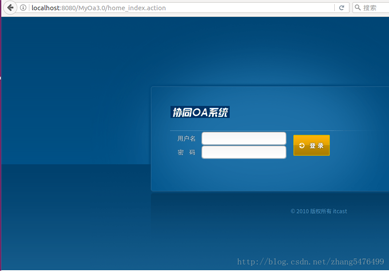
未登录的状态直接输入主页面将自动弹回登录页面,如图所示
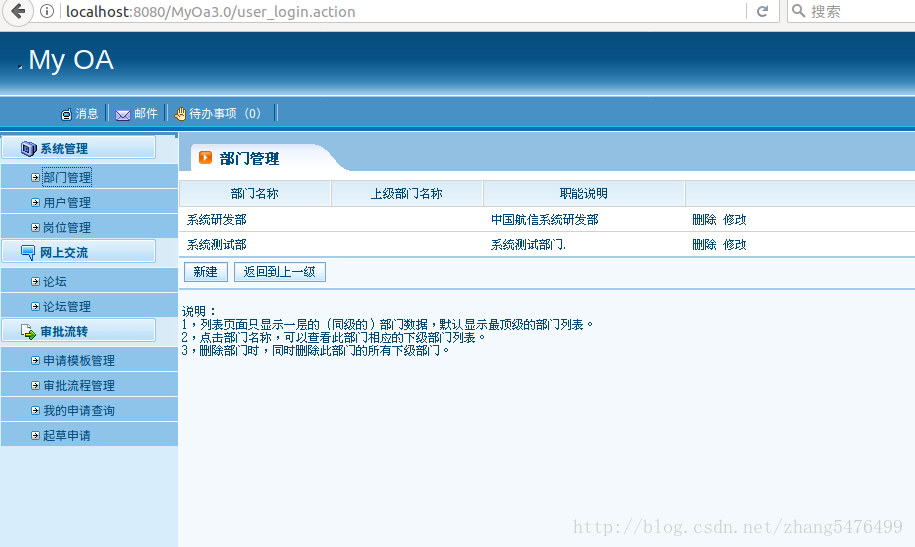
在登录状态下权限如图:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/shizongger/p/6809021.html