一、异步执行
实现方式二种:
1.使用异步注解@aysnc、启动类:添加@EnableAsync注解
2.JDK 8本身有一个非常好用的Future类——CompletableFuture
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
@AllArgsConstructorpublic class AskThread implements Runnable{ private CompletableFuture<Integer> re = null; public void run() { int myRe = 0; try { myRe = re.get() * re.get(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(myRe); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final CompletableFuture<Integer> future = new CompletableFuture<>(); new Thread(new AskThread(future)).start(); //模拟长时间的计算过程 Thread.sleep(1000); //告知完成结果 future.complete(60); }} |
在该示例中,启动一个线程,此时AskThread对象还没有拿到它需要的数据,执行到 myRe = re.get() * re.get()会阻塞。我们用休眠1秒来模拟一个长时间的计算过程,并将计算结果告诉future执行结果,AskThread线程将会继续执行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class Calc { public static Integer calc(Integer para) { try { //模拟一个长时间的执行 Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return para * para; } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { final CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> calc(50)) .thenApply((i) -> Integer.toString(i)) .thenApply((str) -> "\"" + str + "\"") .thenAccept(System.out::println); future.get(); }} |
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync方法构造一个CompletableFuture实例,在supplyAsync()方法中,它会在一个新线程中,执行传入的参数。在这里它会执行calc()方法,这个方法可能是比较慢的,但这并不影响CompletableFuture实例的构造速度,supplyAsync()会立即返回。
而返回的CompletableFuture实例就可以作为这次调用的契约,在将来任何场合,用于获得最终的计算结果。supplyAsync用于提供返回值的情况,CompletableFuture还有一个不需要返回值的异步调用方法runAsync(Runnable runnable),一般我们在优化Controller时,使用这个方法比较多。
这两个方法如果在不指定线程池的情况下,都是在ForkJoinPool.common线程池中执行,而这个线程池中的所有线程都是Daemon(守护)线程,所以,当主线程结束时,这些线程无论执行完毕都会退出系统。
核心代码:
|
1
2
3
|
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> this.afterBetProcessor(betRequest,betDetailResult,appUser,id)); |
异步调用使用Callable来实现
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
@RestControllerpublic class HelloController { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class); @Autowired private HelloService hello; @GetMapping("/helloworld") public String helloWorldController() { return hello.sayHello(); } /** * 异步调用restful * 当controller返回值是Callable的时候,springmvc就会启动一个线程将Callable交给TaskExecutor去处理 * 然后DispatcherServlet还有所有的spring拦截器都退出主线程,然后把response保持打开的状态 * 当Callable执行结束之后,springmvc就会重新启动分配一个request请求,然后DispatcherServlet就重新 * 调用和处理Callable异步执行的返回结果, 然后返回视图 * * @return */ @GetMapping("/hello") public Callable<String> helloController() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入helloController方法"); Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入call方法"); String say = hello.sayHello(); logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 从helloService方法返回"); return say; } }; logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 从helloController方法返回"); return callable; } } |
异步调用的方式 WebAsyncTask
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
@RestControllerpublic class HelloController { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class); @Autowired private HelloService hello; /** * 带超时时间的异步请求 通过WebAsyncTask自定义客户端超时间 * * @return */ @GetMapping("/world") public WebAsyncTask<String> worldController() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入helloController方法"); // 3s钟没返回,则认为超时 WebAsyncTask<String> webAsyncTask = new WebAsyncTask<>(3000, new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入call方法"); String say = hello.sayHello(); logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 从helloService方法返回"); return say; } }); logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 从helloController方法返回"); webAsyncTask.onCompletion(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 执行完毕"); } }); webAsyncTask.onTimeout(new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " onTimeout"); // 超时的时候,直接抛异常,让外层统一处理超时异常 throw new TimeoutException("调用超时"); } }); return webAsyncTask; } /** * 异步调用,异常处理,详细的处理流程见MyExceptionHandler类 * * @return */ @GetMapping("/exception") public WebAsyncTask<String> exceptionController() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入helloController方法"); Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入call方法"); throw new TimeoutException("调用超时!"); } }; logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 从helloController方法返回"); return new WebAsyncTask<>(20000, callable); } } |
二、增加内嵌Tomcat的最大连接数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
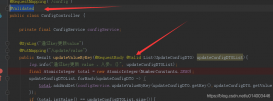
@Configurationpublic class TomcatConfig { @Bean public ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory webServerFactory() { TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatFactory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(); tomcatFactory.addConnectorCustomizers(new MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer()); tomcatFactory.setPort(8005); tomcatFactory.setContextPath("/api-g"); return tomcatFactory; } class MyTomcatConnectorCustomizer implements TomcatConnectorCustomizer { public void customize(Connector connector) { Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler(); //设置最大连接数 protocol.setMaxConnections(20000); //设置最大线程数 protocol.setMaxThreads(2000); protocol.setConnectionTimeout(30000); } }} |
三、使用@ComponentScan()定位扫包比@SpringBootApplication扫包更快
四、默认tomcat容器改为Undertow(Jboss下的服务器,Tomcat吞吐量5000,Undertow吞吐量8000)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion></exclusions> |
改为:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId></dependency> |
五、使用 BufferedWriter 进行缓冲
六、Deferred方式实现异步调用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
@RestControllerpublic class AsyncDeferredController { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); private final LongTimeTask taskService; @Autowired public AsyncDeferredController(LongTimeTask taskService) { this.taskService = taskService; } @GetMapping("/deferred") public DeferredResult<String> executeSlowTask() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进入executeSlowTask方法"); DeferredResult<String> deferredResult = new DeferredResult<>(); // 调用长时间执行任务 taskService.execute(deferredResult); // 当长时间任务中使用deferred.setResult("world");这个方法时,会从长时间任务中返回,继续controller里面的流程 logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "从executeSlowTask方法返回"); // 超时的回调方法 deferredResult.onTimeout(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " onTimeout"); // 返回超时信息 deferredResult.setErrorResult("time out!"); } }); // 处理完成的回调方法,无论是超时还是处理成功,都会进入这个回调方法 deferredResult.onCompletion(new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " onCompletion"); } }); return deferredResult; }} |
七、异步调用可以使用AsyncHandlerInterceptor进行拦截
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
@Componentpublic class MyAsyncHandlerInterceptor implements AsyncHandlerInterceptor { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAsyncHandlerInterceptor.class); @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {// HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "服务调用完成,返回结果给客户端"); } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { if(null != ex){ System.out.println("发生异常:"+ex.getMessage()); } } @Override public void afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { // 拦截之后,重新写回数据,将原来的hello world换成如下字符串 String resp = "my name is chhliu!"; response.setContentLength(resp.length()); response.getOutputStream().write(resp.getBytes()); logger.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 进入afterConcurrentHandlingStarted方法"); } } |
以上这篇基于Springboot吞吐量优化解决方案就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32447301/article/details/88046026