情景描述
一个聚合项目spring-security-tutorial,其中包括4个module,pom如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.github.jdkong.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-tutorial</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>pom</packaging> <modules>`` <module>security-core</module> <module>security-app</module> <module>security-browser</module> <module>security-demo</module> </modules> <!-- 其他部分省略--></project> |
在此项目中,子项目security-browser是一个简单的maven项目,打成jar包,供security-demo使用,security-demo项目是一个springboot项目。
问题描述
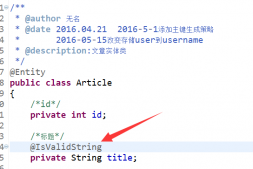
在security-browser项目中自动注入了一个配置类,如下所示:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/** * @author jdkong */@Slf4j@Configurationpublic class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.formLogin() .and() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest() .authenticated(); }} |
在security-demo中使用此配置类时,不起作用。
问题分析
导致此类问题的主要原因是,此类不在Spring Boot的组件扫描范围之内。
1. 关于 Spring Boot 自动注入及组件扫描
在平时使用 Spring Boot 时,常常会使用到@Configuration,@Contoller,@Service,@Component等注解,被添加这些注解的类,在 Spring Boot 启动时,会自动被 Spring 容器管理起来。
上面提到了,添加了一些注解的类会在Spring Boot 容器启动时,被加载到Spring 容器中。那么,组件扫描的作用就是:当 Spring Boot 启动时,根据定义的扫描路径,把符合扫描规则的类装配到spring容器中。
2. Spring Boot 中 @ComponentScan
简单的介绍了@ComponentScan的基础作用,这个注解为我们使用提供了一些可自定义配置属性,先来看看@ComponentScan注解源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target({ElementType.TYPE})@Documented@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)public @interface ComponentScan { // 指定扫描包的位置(同:basePackages 属性),可以是单个路径,也可以是扫描的路径数组 @AliasFor("basePackages") String[] value() default {}; // 指定扫描包的位置(同:value 属性) @AliasFor("value") String[] basePackages() default {}; // 指定具体的扫描的类 Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {}; // bean的名称的生成器 Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class; Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class; ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT; // 控制符合组件检测条件的类文件 默认是包扫描下的 **/*.class String resourcePattern() default "**/*.class"; // 是否开启对@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller的类进行检测 boolean useDefaultFilters() default true; // 包含的过滤条件 // 1. FilterType.ANNOTATION: 按照注解过滤 // 2. FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE: 按照给定的类型 // 3. FilterType.ASPECTJ: 使用ASPECTJ表达式 // 4. FilterType.REGEX: 正则 // 5. FilterType.CUSTOM: 自定义规则 ComponentScan.Filter[] includeFilters() default {}; // 排除的过滤条件,用法和includeFilters一样 ComponentScan.Filter[] excludeFilters() default {}; boolean lazyInit() default false; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({}) public @interface Filter { FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION; @AliasFor("classes") Class<?>[] value() default {}; @AliasFor("value") Class<?>[] classes() default {}; String[] pattern() default {}; }} |
总结一下@ComponentScan的常用方式如下:
通过使用value,basePackages属性来指定扫描范围;
自定扫描路径下边带有@Controller,@Service,@Repository,@Component注解加入Spring容器
通过includeFilters加入扫描路径下没有以上注解的类加入spring容器
通过excludeFilters过滤出不用加入spring容器的类
自定义增加了@Component注解的注解方式
3. Spring Boot 中 @SpringBootApplication
在创建Spring Boot 项目之后,在默认的启动类上会被添加@SpringBootApplication注解,这个注解默认帮我们开启一些自动配置的功能,比如:基于Java的Spring配置,组件扫描,特别是用于启用Spring Boot的自动配置功能。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documented@Inherited@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration // 允许自动配置@ComponentScan( excludeFilters = {@Filter( // 定义排除规则 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, // 采用自定义的方式 classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} // 自定义实现逻辑), @Filter( // 同上 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class})})public @interface SpringBootApplication { // 为 @EnableAutoConfiguration 添加 exclude 规则 @AliasFor( annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "exclude" ) Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; // 为 @EnableAutoConfiguration 添加 excludeName 规则 @AliasFor( annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "excludeName" ) String[] excludeName() default {}; // 为 @ComponentScan 添加 basePackages 规则 @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages" ) String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; // 为 @ComponentScan 添加 basePackageClasses 规则 @AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses" ) Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};} |
从上面的源码部分可以看到,@SpringBootApplication是一个组合注解,也就相当于使用一个@SpringBootApplication可以替代@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan几个注解联合使用。
注:此注释从SpringBoot 1.2开始提供,这意味着如果你运行的是较低的版本,并且如果你需要这些功能,你需要手动添加@Configuration,@CompnentScan和@EnableAutoConfiguration。
那么,可能会有这样的问题,我只是使用了一个@SpringBootApplication注解,但是我如何对@ComponentScan的属性做自定义配置呢?
当然,Spring 团队已经很好的解决了这个问题,在@SpringBootApplication注解类中的属性上添加@AliasFor注解,从而实现通过对@SpringBootApplication中的属性进行自定义,达到对对应的注解的属性的自定义。
比如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@AliasFor( annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; |
这段代码就是实现,通过对@SpringBootApplication的属性scanBasePackages,实现对@ComponentScan中的属性basePackages进行自定义。
4. 回答开篇问题
先看看项目结构,项目入口文件在子项目security-demo中,并且入口类所在包位置为:package com.github.jdkong.security。
也就是说,在不做任何配置的情况下,此项目只会扫描当前包路径及其子路径下的文件,并将符合条件的对象注入到容器中管理。
再看看配置文件所在的包路径位置:package com.github.jdkong.browser.config,可见此包路径并不在项目扫描的路径范围之内。
这也就导致了,我们定义的配置类,虽然加了@Configuration也不会对我们的项目起到作用。
可以对项目注解进行稍微修改,制定扫描包的范围,就可以简单的解决这个问题。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.github.jdkong")public class SecurityApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SecurityApplication.class,args); }} |
5. 补充说明:@AliasFor
在Spring注解中,经常会发现很多注解的不同属性起着相同的作用,比如@ComponentScan的value属性和basePackages属性。所以在使用的时候就需要做一些基本的限制,比如value和basePackages的值不能冲突,比如任意设置value或者设置basePackages属性的值,都能够通过另一个属性来获取值等等。为了统一处理这些情况,Spring创建了@AliasFor标签。
以上这篇解决Spring Boot 多模块注入访问不到jar包中的Bean问题就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41540822/article/details/88852973