本文将详细展示一个多类支持向量机分类器训练iris数据集来分类三种花。
svm算法最初是为二值分类问题设计的,但是也可以通过一些策略使得其能进行多类分类。主要的两种策略是:一对多(one versus all)方法;一对一(one versus one)方法。
一对一方法是在任意两类样本之间设计创建一个二值分类器,然后得票最多的类别即为该未知样本的预测类别。但是当类别(k类)很多的时候,就必须创建k!/(k-2)!2!个分类器,计算的代价还是相当大的。
另外一种实现多类分类器的方法是一对多,其为每类创建一个分类器。最后的预测类别是具有最大svm间隔的类别。本文将实现该方法。
我们将加载iris数据集,使用高斯核函数的非线性多类svm模型。iris数据集含有三个类别,山鸢尾、变色鸢尾和维吉尼亚鸢尾(i.setosa、i.virginica和i.versicolor),我们将为它们创建三个高斯核函数svm来预测。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
|
# multi-class (nonlinear) svm example#----------------------------------## this function wll illustrate how to# implement the gaussian kernel with# multiple classes on the iris dataset.## gaussian kernel:# k(x1, x2) = exp(-gamma * abs(x1 - x2)^2)## x : (sepal length, petal width)# y: (i. setosa, i. virginica, i. versicolor) (3 classes)## basic idea: introduce an extra dimension to do# one vs all classification.## the prediction of a point will be the category with# the largest margin or distance to boundary.import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom sklearn import datasetsfrom tensorflow.python.framework import opsops.reset_default_graph()# create graphsess = tf.session()# load the data# 加载iris数据集并为每类分离目标值。# 因为我们想绘制结果图,所以只使用花萼长度和花瓣宽度两个特征。# 为了便于绘图,也会分离x值和y值# iris.data = [(sepal length, sepal width, petal length, petal width)]iris = datasets.load_iris()x_vals = np.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data])y_vals1 = np.array([1 if y==0 else -1 for y in iris.target])y_vals2 = np.array([1 if y==1 else -1 for y in iris.target])y_vals3 = np.array([1 if y==2 else -1 for y in iris.target])y_vals = np.array([y_vals1, y_vals2, y_vals3])class1_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==0]class1_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==0]class2_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==1]class2_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==1]class3_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==2]class3_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==2]# declare batch sizebatch_size = 50# initialize placeholders# 数据集的维度在变化,从单类目标分类到三类目标分类。# 我们将利用矩阵传播和reshape技术一次性计算所有的三类svm。# 注意,由于一次性计算所有分类,# y_target占位符的维度是[3,none],模型变量b初始化大小为[3,batch_size]x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[none, 2], dtype=tf.float32)y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[3, none], dtype=tf.float32)prediction_grid = tf.placeholder(shape=[none, 2], dtype=tf.float32)# create variables for svmb = tf.variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[3,batch_size]))# gaussian (rbf) kernel 核函数只依赖x_datagamma = tf.constant(-10.0)dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1)dist = tf.reshape(dist, [-1,1])sq_dists = tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data)))my_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(sq_dists)))# declare function to do reshape/batch multiplication# 最大的变化是批量矩阵乘法。# 最终的结果是三维矩阵,并且需要传播矩阵乘法。# 所以数据矩阵和目标矩阵需要预处理,比如xt·x操作需额外增加一个维度。# 这里创建一个函数来扩展矩阵维度,然后进行矩阵转置,# 接着调用tensorflow的tf.batch_matmul()函数def reshape_matmul(mat): v1 = tf.expand_dims(mat, 1) v2 = tf.reshape(v1, [3, batch_size, 1]) return(tf.matmul(v2, v1))# compute svm model 计算对偶损失函数first_term = tf.reduce_sum(b)b_vec_cross = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(b), b)y_target_cross = reshape_matmul(y_target)second_term = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(my_kernel, tf.multiply(b_vec_cross, y_target_cross)),[1,2])loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.negative(tf.subtract(first_term, second_term)))# gaussian (rbf) prediction kernel# 现在创建预测核函数。# 要当心reduce_sum()函数,这里我们并不想聚合三个svm预测,# 所以需要通过第二个参数告诉tensorflow求和哪几个ra = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1),[-1,1])rb = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(prediction_grid), 1),[-1,1])pred_sq_dist = tf.add(tf.subtract(ra, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(prediction_grid)))), tf.transpose(rb))pred_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(pred_sq_dist)))# 实现预测核函数后,我们创建预测函数。# 与二类不同的是,不再对模型输出进行sign()运算。# 因为这里实现的是一对多方法,所以预测值是分类器有最大返回值的类别。# 使用tensorflow的内建函数argmax()来实现该功能prediction_output = tf.matmul(tf.multiply(y_target,b), pred_kernel)prediction = tf.arg_max(prediction_output-tf.expand_dims(tf.reduce_mean(prediction_output,1), 1), 0)accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, tf.argmax(y_target,0)), tf.float32))# declare optimizermy_opt = tf.train.gradientdescentoptimizer(0.01)train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)# initialize variablesinit = tf.global_variables_initializer()sess.run(init)# training looploss_vec = []batch_accuracy = []for i in range(100): rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size) rand_x = x_vals[rand_index] rand_y = y_vals[:,rand_index] sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y, prediction_grid:rand_x}) batch_accuracy.append(acc_temp) if (i+1)%25==0: print('step #' + str(i+1)) print('loss = ' + str(temp_loss))# 创建数据点的预测网格,运行预测函数x_min, x_max = x_vals[:, 0].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = x_vals[:, 1].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 1].max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02), np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]grid_predictions = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y, prediction_grid: grid_points})grid_predictions = grid_predictions.reshape(xx.shape)# plot points and gridplt.contourf(xx, yy, grid_predictions, cmap=plt.cm.paired, alpha=0.8)plt.plot(class1_x, class1_y, 'ro', label='i. setosa')plt.plot(class2_x, class2_y, 'kx', label='i. versicolor')plt.plot(class3_x, class3_y, 'gv', label='i. virginica')plt.title('gaussian svm results on iris data')plt.xlabel('pedal length')plt.ylabel('sepal width')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.ylim([-0.5, 3.0])plt.xlim([3.5, 8.5])plt.show()# plot batch accuracyplt.plot(batch_accuracy, 'k-', label='accuracy')plt.title('batch accuracy')plt.xlabel('generation')plt.ylabel('accuracy')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.show()# plot loss over timeplt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')plt.title('loss per generation')plt.xlabel('generation')plt.ylabel('loss')plt.show() |
输出:
instructions for updating:
use `argmax` instead
step #25
loss = -313.391
step #50
loss = -650.891
step #75
loss = -988.39
step #100
loss = -1325.89

山鸢尾花(i.setosa)非线性高斯svm模型的多分类(三类)结果,其中gamma值为10

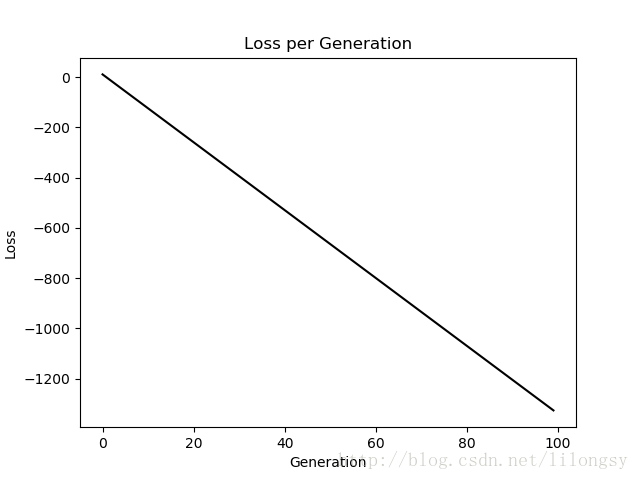
重点是改变svm算法一次性优化三类svm模型。模型参数b通过增加一个维度来计算三个模型。我们可以看到,使用tensorflow内建功能可以轻松扩展算法到多类的相似算法。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/lilongsy/article/details/79420081