引言:循环依赖就是N个类中循环嵌套引用,如果在日常开发中我们用new 对象的方式发生这种循环依赖的话程序会在运行时一直循环调用,直至内存溢出报错。下面说一下spring是如果解决循环依赖的。
第一种:构造器参数循环依赖
Spring容器会将每一个正在创建的Bean 标识符放在一个“当前创建Bean池”中,Bean标识符在创建过程中将一直保持
在这个池中,因此如果在创建Bean过程中发现自己已经在“当前创建Bean池”里时将抛出
BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常表示循环依赖;而对于创建完毕的Bean将从“当前创建Bean池”中清除掉。
首先我们先初始化三个Bean。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class StudentA { private StudentB studentB ; public void setStudentB(StudentB studentB) { this.studentB = studentB; } public StudentA() { } public StudentA(StudentB studentB) { this.studentB = studentB; } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class StudentB { private StudentC studentC ; public void setStudentC(StudentC studentC) { this.studentC = studentC; } public StudentB() { } public StudentB(StudentC studentC) { this.studentC = studentC; } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public class StudentC { private StudentA studentA ; public void setStudentA(StudentA studentA) { this.studentA = studentA; } public StudentC() { } public StudentC(StudentA studentA) { this.studentA = studentA; } } |
OK,上面是很基本的3个类,,StudentA有参构造是StudentB。StudentB的有参构造是StudentC,StudentC的有参构造是StudentA ,这样就产生了一个循环依赖的情况,
我们都把这三个Bean交给Spring管理,并用有参构造实例化
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<bean id="a" class="com.zfx.student.StudentA"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="b"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="b" class="com.zfx.student.StudentB"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="c"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="c" class="com.zfx.student.StudentC"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="a"></constructor-arg> </bean> |
下面是测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/zfx/student/applicationContext.xml"); //System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class)); } } |
执行结果报错信息为:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException:
Error creating bean with name 'a': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
如果大家理解开头那句话的话,这个报错应该不惊讶,Spring容器先创建单例StudentA,StudentA依赖StudentB,然后将A放在“当前创建Bean池”中,此时创建StudentB,StudentB依赖StudentC ,然后将B放在“当前创建Bean池”中,此时创建StudentC,StudentC又依赖StudentA, 但是,此时Student已经在池中,所以会报错,,因为在池中的Bean都是未初始化完的,所以会依赖错误 ,(初始化完的Bean会从池中移除)
第二种:setter方式单例,默认方式
如果要说setter方式注入的话,我们最好先看一张Spring中Bean实例化的图
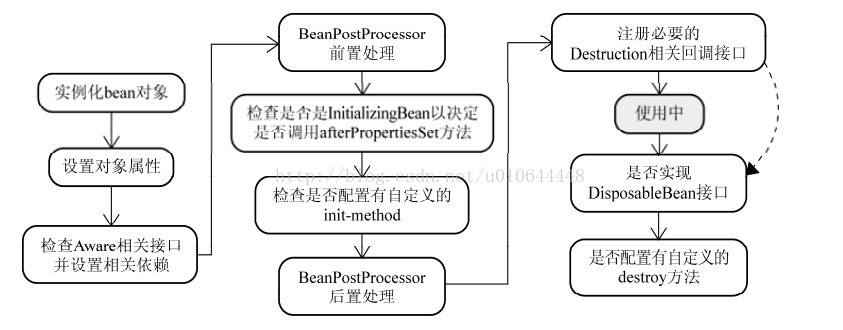
如图中前两步骤得知:Spring是先将Bean对象实例化之后再设置对象属性的
修改配置文件为set方式注入:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<!--scope="singleton"(默认就是单例方式) --><bean id="a" class="com.zfx.student.StudentA" scope="singleton"> <property name="studentB" ref="b"></property> </bean> <bean id="b" class="com.zfx.student.StudentB" scope="singleton"> <property name="studentC" ref="c"></property> </bean> <bean id="c" class="com.zfx.student.StudentC" scope="singleton"> <property name="studentA" ref="a"></property> </bean> |
下面是测试类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/zfx/student/applicationContext.xml"); System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class)); } } |
打印结果为:
com.zfx.student.StudentA@1fbfd6
为什么用set方式就不报错了呢 ?
我们结合上面那张图看,Spring先是用构造实例化Bean对象 ,此时Spring会将这个实例化结束的对象放到一个Map中,并且Spring提供了获取这个未设置属性的实例化对象引用的方法。 结合我们的实例来看,,当Spring实例化了StudentA、StudentB、StudentC后,紧接着会去设置对象的属性,此时StudentA依赖StudentB,就会去Map中取出存在里面的单例StudentB对象,以此类推,不会出来循环的问题喽、
下面是Spring源码中的实现方法,。以下的源码在Spring的Bean包中的DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.Java类中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance(缓存单例实例化对象的Map集合) */ private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(64); /** Cache of singleton factories: bean name --> ObjectFactory(单例的工厂Bean缓存集合) */ private final Map<String, ObjectFactory> singletonFactories = new HashMap<String, ObjectFactory>(16); /** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name --> bean instance(早期的单身对象缓存集合) */ private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<String, Object>(16); /** Set of registered singletons, containing the bean names in registration order(单例的实例化对象名称集合) */ private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(64); /** * 添加单例实例 * 解决循环引用的问题 * Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton * if necessary. * <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to * resolve circular references. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object */ protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) { this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory); this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } } } |
第三种:setter方式原型,prototype
修改配置文件为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<bean id="a" class="com.zfx.student.StudentA" <span style="color:#FF0000;">scope="prototype"</span>> <property name="studentB" ref="b"></property> </bean> <bean id="b" class="com.zfx.student.StudentB" <span style="color:#FF0000;">scope="prototype"</span>> <property name="studentC" ref="c"></property> </bean> <bean id="c" class="com.zfx.student.StudentC" <span style="color:#FF0000;">scope="prototype"</span>> <property name="studentA" ref="a"></property> </bean> |
scope="prototype" 意思是 每次请求都会创建一个实例对象。两者的区别是:有状态的bean都使用Prototype作用域,无状态的一般都使用singleton单例作用域。
测试用例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/zfx/student/applicationContext.xml"); <strong>//此时必须要获取Spring管理的实例,因为现在scope="prototype" 只有请求获取的时候才会实例化对象</strong> System.out.println(context.getBean("a", StudentA.class)); } } |
打印结果:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'a': Requested bean is currently in creation: Is there an unresolvable circular reference?
为什么原型模式就报错了呢 ?
对于“prototype”作用域Bean,Spring容器无法完成依赖注入,因为“prototype”作用域的Bean,Spring容
器不进行缓存,因此无法提前暴露一个创建中的Bean。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/1ning/p/6963869.html