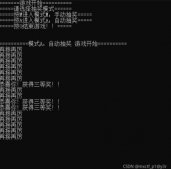
简单工厂模式实例
题目:实现计算器的输入2个数和运算符,得到结果
工程结构:
(1)头文件
COperationFactory.h(运算符工厂类)
(2)源文件
SimpleFactory.cpp(客户端应用类,主函数所在)
(3)运算类
COperation.cpp(运算符基类)
COperation.h
COperationAdd.h(加法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
COperationDiv.h (除法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
COperationMul.h (乘法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
COperationSub.h(减法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
============= 代码实现部分 =============
COperationFactory.h(运算符工厂类)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
/************************************************************************//* 运算符工厂类 *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _OPERATION_FACTORY_H_ #define _OPERATION_FACTORY_H_ #include "stdafx.h" #include "COperation.h" #include "COperationAdd.h" #include "COperationSub.h" #include "COperationMul.h" #include "COperationDiv.h" #include "COperationFactory.h" class COperationFactory { public: COperationFactory(){}; ~COperationFactory(){}; // 根据入参的不同,创建其对应的运算符类指针。就像是个工厂,创建用户指定的运算符类指针 static COperation* NewOperation(const string& strOperate) { // 入参合法性判断,防止后面的strOperate[0]发生越界访问 if (strOperate.size() != 1) { return NULL; } COperation* pOperation = NULL; switch (strOperate[0]) { case '+': pOperation = new COperationAdd(); break; case '-': pOperation = new COperationSub(); break; case '*': pOperation = new COperationMul(); break; case '/': pOperation = new COperationDiv(); break; default: break; } return pOperation; }; }; #endif _OPERATION_FACTORY_H_ |
COperation.cpp(运算符基类)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#include "stdafx.h" #include "COperation.h" COperation::COperation() : _dNumA(0) , _dNumB(0) { } |
COperation.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
/************************************************************************//* 运算符基类 *//************************************************************************/ #ifndef _COPERATION_H_ #define _COPERATION_H_ class COperation { public: COperation(); ~COperation(){}; // 设置被运算数 void SetNumA(double dNumA) { _dNumA = dNumA; }; // 获取被运算数 double GetNumA() { return _dNumA; }; // 设置运算数 void SetNumB(double dNumB) { _dNumB = dNumB; }; // 获取运算数 double GetNumB() { return _dNumB; }; // 计算结果且在子类中实现各自的运算方法结果 virtual double Result() { double dResult = 0; return dResult; } private: double _dNumA; double _dNumB; }; #endif _COPERATION_H_ |
COperationAdd.h(加法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/************************************************************************//* 加法运算符子类,继承于运算符基类 *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _COPERATION_ADD_H_ #define _COPERATION_ADD_H_ #include "COperation.h" class COperationAdd : public COperation { public: COperationAdd(){}; ~COperationAdd(){}; double Result() { return (GetNumA() + GetNumB()); }; }; #endif _COPERATION_ADD_H_ |
COperationDiv.h (除法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/************************************************************************//* 除法运算符子类,继承于运算符基类 *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _COPERATION_DIV_H_ #define _COPERATION_DIV_H_ #include "COperation.h" class COperationDiv : public COperation { public: COperationDiv(){}; ~COperationDiv(){}; double Result() { double dResult = 0; if (0 != GetNumB()) { dResult = (GetNumA() / GetNumB()); } else { cout << "error: divisor is "; } return dResult; }; }; #endif _COPERATION_DIV_H_ |
COperationMul.h (乘法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/************************************************************************//* 乘法运算符子类,继承于运算符基类 *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _COPERATION_MUL_H_ #define _COPERATION_MUL_H_ #include "COperation.h" class COperationMul : public COperation { public: COperationMul(){}; ~COperationMul(){}; double Result() { return (GetNumA() * GetNumB()); }; }; #endif _COPERATION_MUL_H_ |
COperationSub.h(减法运算符子类,继承于COperation)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/************************************************************************//* 减法运算符子类,继承于运算符基类 *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _COPERATION_SUB_H_ #define _COPERATION_SUB_H_ #include "COperation.h" class COperationSub : public COperation { public: COperationSub(){}; ~COperationSub(){}; double Result() { return (GetNumA() - GetNumB()); }; }; #endif _COPERATION_SUB_H_ |
SimpleFactory.cpp(客户端应用类,主函数所在)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
// SimpleFactory.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include "COperationFactory.h" int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { // 通过运算符工厂创建加法运算 COperation* OperAdd = COperationFactory::NewOperation("+"); if (NULL != OperAdd) { OperAdd->SetNumA(168); // 设置被加数 OperAdd->SetNumB(105); // 设置加数 cout << "168 + 105 = " << (OperAdd->Result()) << endl; } // 通过运算符工厂创建减法运算 COperation* OperSub = COperationFactory::NewOperation("-"); if (NULL != OperSub) { OperSub->SetNumA(168); // 设置被减数 OperSub->SetNumB(105); // 设置减数 cout << "168 - 105 = " << (OperSub->Result()) << endl; } // 通过运算符工厂创建乘法运算 COperation* OperMul = COperationFactory::NewOperation("*"); if (NULL != OperMul) { OperMul->SetNumA(168); // 设置被乘数 OperMul->SetNumB(105); // 设置乘数 cout << "168 * 105 = " << (OperMul->Result()) << endl; } // 通过运算符工厂创建除法运算 COperation* OperDiv = COperationFactory::NewOperation("/"); if (NULL != OperDiv) { OperDiv->SetNumA(168); // 设置被除数 OperDiv->SetNumB(105); // 设置除数 cout << "168 / 105 = " << (OperDiv->Result()) << endl; OperDiv->SetNumB(0); // 改变除数 cout << (OperDiv->Result()) << endl; } // 阻止控制台进程结束,便于查看结果 int nEnd = 0; cin >> nEnd; return 0; } |
抽象工厂模式实例
工程结构:
(1)抽象产品类
IFruit.h
(2)抽象工厂类
IFruitGardener.h
(3)具体产品类
CApple.h
CGrape.h
CStrawberry.h
(4)具体工厂类
CAppleGardener.h
CGrapeGardener.h
CStrawberryGardener.h
(5)客户端
FactoryMethodApplication.cpp
(1)抽象产品类
IFruit.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
/************************************************************************//* 抽象水果类(abstract Product) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _IFRUIT_H_ #define _IFRUIT_H_ #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std; class IFruit { public: virtual void grow() = 0; virtual void harvest() = 0; virtual void plant() = 0; }; #endif _IFRUIT_H_ |
(2)抽象工厂类
IFruitGardener.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/************************************************************************//* 抽象水果园丁类(abstract Factory) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _IFRUIT_GARDENER_H_ #define _IFRUIT_GARDENER_H_ #include "IFruit.h" class IFruitGardener { public: virtual IFruit* Factory() = 0; }; #endif _IFRUIT_GARDENER_H_ |
(3)具体产品类
CApple.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的苹果类(Concrete Product) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _APPLE_H_ #define _APPLE_H_ #include "IFruit.h" class CApple : public IFruit { public: void grow() { cout << "Apple is growing..." << endl; }; void harvest() { cout << "Apple has been harvested." << endl; }; void plant() { cout << "Apple has been planted." << endl; }; int GetTreeAge() { return m_iAppleTreeAge; }; void SetTreeAge(const int iAge) { m_iAppleTreeAge = iAge; } private: int m_iAppleTreeAge; }; #endif _APPLE_H_ |
CGrape.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的葡萄类(Concrete Product) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _GRAPE_H_ #define _GRAPE_H_ #include "IFruit.h" class CGrape : public IFruit { public: void grow() { cout << "Grape is growing..." << endl; }; void harvest() { cout << "Grape has been harvested." << endl; }; void plant() { cout << "Grape has been planted." << endl; }; bool GetSeedless() { return m_bSeedless; }; void SetSeedless(const bool bSeedless) { m_bSeedless = bSeedless; }; private: bool m_bSeedless; }; #endif _GRAPE_H_ |
CStrawberry.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的草莓类(Concrete Product) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _STRAWBERRY_H_ #define _STRAWBERRY_H_ #include "IFruit.h" class CStrawberry : public IFruit { public: void grow() { cout << "Strawberry is growing..." << endl; }; void harvest() { cout << "Strawberry has been harvested." << endl; }; void plant() { cout << "Strawberry has been planted." << endl; }; }; #endif _STRAWBERRY_H_ |
(4)具体工厂类
CAppleGardener.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的苹果园丁类(Concrete Factory) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _APPLE_GARDENER_H_ #define _APPLE_GARDENER_H_ #include "IFruitGardener.h" #include "CApple.h" class CAppleGardener : public IFruitGardener { public: CAppleGardener():m_pApple(NULL){}; IFruit* Factory() { if (NULL == m_pApple) { m_pApple = new CApple(); } return m_pApple; }; private: CApple* m_pApple; }; #endif _APPLE_GARDENER_H_ |
CGrapeGardener.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的葡萄园丁类(Concrete Factory) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _GRAPE_GARDENER_H_ #define _GRAPE_GARDENER_H_ #include "IFruitGardener.h" #include "CGrape.h" class CGrapeGardener : public IFruitGardener { public: CGrapeGardener():m_pGrape(NULL){}; IFruit* Factory() { if (NULL == m_pGrape) { m_pGrape = new CGrape(); } return m_pGrape; }; private: CGrape* m_pGrape; }; #endif _GRAPE_GARDENER_H_ |
CStrawberryGardener.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/************************************************************************//* 具体的草莓园丁类(Concrete Factory) *//************************************************************************/#ifndef _STRAWBERRY_GARDENER_H_ #define _STRAWBERRY_GARDENER_H_ #include "IFruitGardener.h" #include "CStrawberry.h" class CStrawberryGardener : public IFruitGardener { public: CStrawberryGardener():m_pStrawberry(NULL){}; IFruit* Factory() { if (NULL == m_pStrawberry) { m_pStrawberry = new CStrawberry(); } return m_pStrawberry; }; private: CStrawberry* m_pStrawberry; }; #endif _STRAWBERRY_GARDENER_H_ |
(5)客户端
FactoryMethodApplication.cpp
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
// FactoryMethodApplication.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <Windows.h> #include "IFruitGardener.h" #include "CAppleGardener.h" #include "CGrapeGardener.h" #include "CStrawberryGardener.h" int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { static IFruitGardener* pFruitFactory1 = NULL; static IFruitGardener* pFruitFactory2 = NULL; static IFruit* pFruit1 = NULL; static IFruit* pFruit2 = NULL; pFruitFactory1 = new CAppleGardener(); if (NULL != pFruitFactory1) { pFruit1 = pFruitFactory1->Factory(); if (NULL != pFruit1) { pFruit1->grow(); pFruit1->harvest(); pFruit1->plant(); } } pFruitFactory2 = new CGrapeGardener(); if (NULL != pFruitFactory2) { pFruit2 = pFruitFactory2->Factory(); if (NULL != pFruit2) { pFruit2->grow(); pFruit2->harvest(); pFruit2->plant(); } } Sleep(10000); return 0; } |
总结
首先无论是简单工厂模式还是工厂方法模式都是把不变的地方提取出来,把容易发生变化的封装起来。以达到做大程度的复用,和适应用户的变动,以及项目的扩展。
一、简单工厂模式
1.理解
又称为静态工厂模式,它专门定义一个类来负责创建其他类的实例,被创建的实例通常都具有相通的父类。由工厂类根据传入的参数动态决定应该创建哪一个产品类的实例。它包含必要的判断逻辑,能根据外界给定的信息,决定应该穿件那个具体类的对象。简单工厂模式可以理解为父亲给儿子留了一笔钱,规定这笔钱可以用于上学、买房或者买车,然后让儿子自己选择用于哪一个。
2.优点
工厂类包含必要的逻辑判断,可以决定在什么时候创建哪一个类的实例,客户端可以避免直接创建对象。这样就可以实现对责任的分割,降低耦合性,明确了具体的职责和权力,有利于整个系统的优化。
3.缺点
当产品具有比较复杂的多层结构时,它的工厂类只有一个,这时候再以不变应万变就成为它最大的缺点了。因为工厂类是整个组织的核心,它聚集了所有产品的创建逻辑,一旦工厂不能正常工作,整个系统都会受到影响,可扩展性较差。扩展性差一旦有新的需求,就不得不修改工厂逻辑,这样就会导致工厂逻辑过为复杂,违背了开——闭原则。同时静态工厂方法不利于形成基于继承的等级结构。
二、工厂方法模式
1.理解
它是一个粒度很小的设计模式,因为模式的表现只是一个抽象的方法。工厂方法模式定义了一个用于创建对象的界面,让子类决定具体实例化哪一个类。也就是在工厂和产品之间增加界面,工厂不再负责产品的实现,有借口针对不同条件返回不同的类实例,再由具体类实例去实现。工厂方法时简单工厂的衍生,改进了许多简单工厂的缺点,遵循了开——闭原则,实现了可扩展,可以用于更为复杂的产品结果场合。工厂方法可以理解为同样是父亲给儿子留了一笔钱,然后直接让儿子去支配,怎么花父亲一律不管。
2.优点
工厂方法模式客服了简单工厂的很多缺点,它每个具体工厂只完成单一任务,而且遵循开——闭原则,代码简洁而且具有良好的扩展性。
3.缺点
如果有产品类需要修改,对应的工厂类也需要进行修改。一旦有多个产品类都需要修改的时候,对号入座的问题就出现了,这是对工厂类的修改就会变得相当复杂。因此工厂方法模式虽然有利于扩展但是不利于维护。
综上所述,我们就可以知道针对不同的情况具体采用哪种模式对编程更有利了。当需要创建的对象比较少,客户只知道传入工厂的参数,并不关心如何创建对象的时候就可以采用简单工厂模式;当类将创建对象的职责委托给多个帮助子类中的某一个时就可以采用工厂方法模式了。