本文实例讲述了java使用备忘录模式实现过关类游戏功能。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
一.模式定义
备忘录模式,在不破坏封闭的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象外部保存这个状态。这样以后就可将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
二.模式举例
1模式分析
我们借用过关类游戏来说明这一模式。
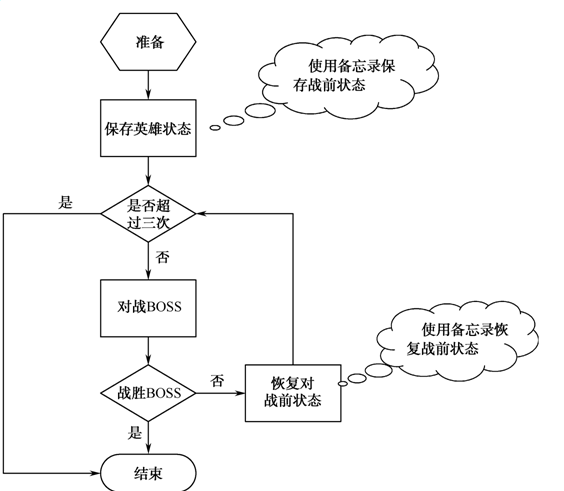
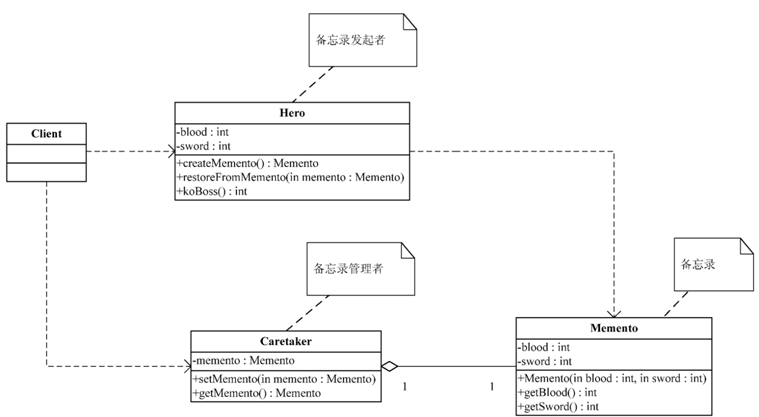
2备忘录模式静态类图
3代码示例(黑箱备忘录模式)
3.1创建备忘录窄接口一inarrowmemento
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
package com.demo.memento;/** * 备忘录窄接口(不提供任何方法,外部对象不能访问备忘录对象内部信息) * * @author * */public interface inarrowmemento {} |
3.2备忘录发起者一hero
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
package com.demo.originator;import java.util.random;import com.demo.memento.inarrowmemento;/** * 挑战者 * * @author * */public class hero { // 血液值 private int blood; // 武力值 private int sword; // 随机数 private final random random = new random(); // 构造方法初始化 内容 public hero() { this.blood = 100; this.sword = 100; } // 创建备忘录保存内容 public inarrowmemento creatememento() { system.out.println("创建备忘录..."); return new memento(this.blood, this.sword); } // 恢复备忘录内容 public void restorefrommemento(inarrowmemento memento) { system.out.println("恢复备忘录中的状态..."); if (memento != null) { memento memento2 = (memento) memento; this.blood = memento2.getblood(); this.sword = memento2.getsword(); } } /** * 挑战boss */ public int koboss() { // 当血液值<=0 时 挑战失败 假设战胜boss的概率为2% // 判断时候还有血液值 if (this.blood <= 0 || this.sword <= 0) { system.out.println(this.tostring()); system.out.println("挑战boss失败!"); return -1; } else { // 获得随机数 double win = math.random(); if (win <= 0.02) { system.out.println(this.tostring()); system.out.println("恭喜你,挑战boss成功!"); return 1; } else { system.out.println(this.tostring()); system.out.println("继续攻击boss..."); // 随机数减少血液值和武力值 继续ko int blood_sub = random.nextint(10); int sword_sub = random.nextint(10); this.blood -= blood_sub; this.sword -= sword_sub; return 0; } } } @override public string tostring() { return "当前血液值:" + this.blood + " - 当前武力值:" + this.sword; } /** * 备忘录(整个类都是私有的,只有发起者才能访问) * * @author * */ private class memento implements inarrowmemento { // 血液值 private final int blood; // 武力值 private final int sword; // 构造方法初始化 内容 private memento(int blood, int sword) { this.blood = blood; this.sword = sword; } private int getblood() { return blood; } private int getsword() { return sword; } }} |
3.3备忘录管理者一caretaker
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package com.demo.caretaker;import com.demo.memento.inarrowmemento;/** * 管理者 * * @author * */public class caretaker { private inarrowmemento memento; /** * 获得备忘录对象 * * @return */ public inarrowmemento getmemento() { return memento; } /** * 保存备忘录对象 * * @param memento */ public void setmemento(inarrowmemento memento) { this.memento = memento; }} |
3.4让英雄挑战boss一client
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
package com.demo;import com.demo.caretaker.caretaker;import com.demo.originator.hero;/** * 客户端主应用程序 * * @author * */public class client { /** * @param args */ public static void main(string[] args) { // 创建角色 hero hero = new hero(); // 创建管理者 caretaker caretaker = new caretaker(); // 保存挑战前的状态信息 caretaker.setmemento(hero.creatememento()); // 只有三次战胜boss的机会 int cnt = 1; // 挑战boss结果 int ko = -1; while (ko != 1 && cnt <= 3) { system.out .println("=============== 第" + cnt + "次挑战 =============="); // 开始挑战boss ko = hero.koboss(); while (true) { if (ko == -1) { // 挑战失败 恢复到初始状态 累加挑战次数 hero.restorefrommemento(caretaker.getmemento()); cnt += 1; break; } else if (ko == 0) { // 继续挑战 ko = hero.koboss(); } else if (ko == 1) { // 挑战成功! break; } } } }} |
4运行结果
创建备忘录...
=============== 第1次挑战 ==============
当前血液值:100 - 当前武力值:100
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:96 - 当前武力值:99
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:90 - 当前武力值:98
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:81 - 当前武力值:95
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:78 - 当前武力值:93
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:72 - 当前武力值:88
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:64 - 当前武力值:85
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:56 - 当前武力值:80
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:49 - 当前武力值:73
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:45 - 当前武力值:71
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:37 - 当前武力值:68
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:29 - 当前武力值:65
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:20 - 当前武力值:59
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:11 - 当前武力值:54
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:9 - 当前武力值:52
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:3 - 当前武力值:45
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:-3 - 当前武力值:41
挑战boss失败!
恢复备忘录中的状态...
=============== 第2次挑战 ==============
当前血液值:100 - 当前武力值:100
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:96 - 当前武力值:95
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:96 - 当前武力值:91
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:88 - 当前武力值:82
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:79 - 当前武力值:79
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:76 - 当前武力值:72
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:73 - 当前武力值:70
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:72 - 当前武力值:66
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:72 - 当前武力值:61
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:72 - 当前武力值:58
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:72 - 当前武力值:52
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:63 - 当前武力值:51
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:62 - 当前武力值:50
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:54 - 当前武力值:41
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:50 - 当前武力值:39
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:47 - 当前武力值:39
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:43 - 当前武力值:38
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:37 - 当前武力值:36
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:34 - 当前武力值:35
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:32 - 当前武力值:27
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:28 - 当前武力值:22
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:26 - 当前武力值:15
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:24 - 当前武力值:11
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:19 - 当前武力值:3
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:10 - 当前武力值:-3
挑战boss失败!
恢复备忘录中的状态...
=============== 第3次挑战 ==============
当前血液值:100 - 当前武力值:100
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:99 - 当前武力值:93
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:98 - 当前武力值:84
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:98 - 当前武力值:82
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:95 - 当前武力值:76
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:88 - 当前武力值:68
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:81 - 当前武力值:64
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:76 - 当前武力值:64
继续攻击boss...
当前血液值:67 - 当前武力值:64
恭喜你,挑战boss成功!
三. 该模式设计原则
1封装边界的保持
2双重接口实现,保证安全性。
四. 使用场合
1需要在某一时刻恢复一个对象先前的状态时。
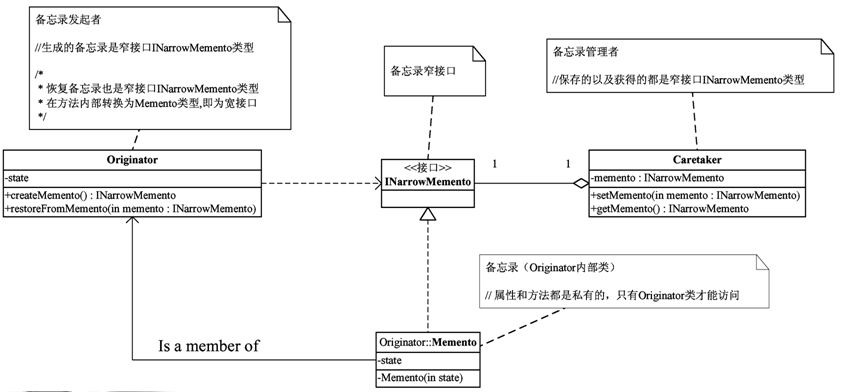
2白箱备忘录模式,需要在外部保存对象某一时刻的状态,但如果用一个接口来让其他对象直接得到这些状态,将会暴露对象的实现细节并破坏对象的封装性。
3黑箱备忘录模式实现方式提供了双重接口访问机制,对发起者对象提供宽接口,而对发起者以外的对象提供窄接口,从而有效解决了封装性和安全性。
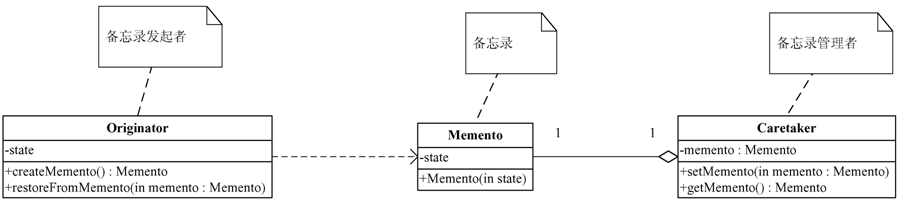
五. 静态类图
1白箱备忘录模式静态类图
2黑箱备忘录模式静态类图
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/chengqiuming/article/details/70139484