free函数是我们再写C语言程序时常用的函数,但是使用时需要注意,一不小心很肯能会引起吐核。
注意:free函数与malloc()函数配对使用,释放malloc函数申请的动态内存。对于free(p)这句语句,如果p 是NULL 指针,那么free 对p 无论操作多少次都不会出问题。如果p 不是NULL 指针,那么free 对p连续操作两次就会导致程序运行错误。
看一个程序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>int main(){ char * name = NULL; free(name); free(name); free(name); printf("no problem11111111\n"); name = (char *) malloc(10); if(name) { printf("allocate successful\n"); } else { printf("allocate failed\n"); } free(name); free(name); printf("no problem2222222\n"); return 0;} |
运行结果:
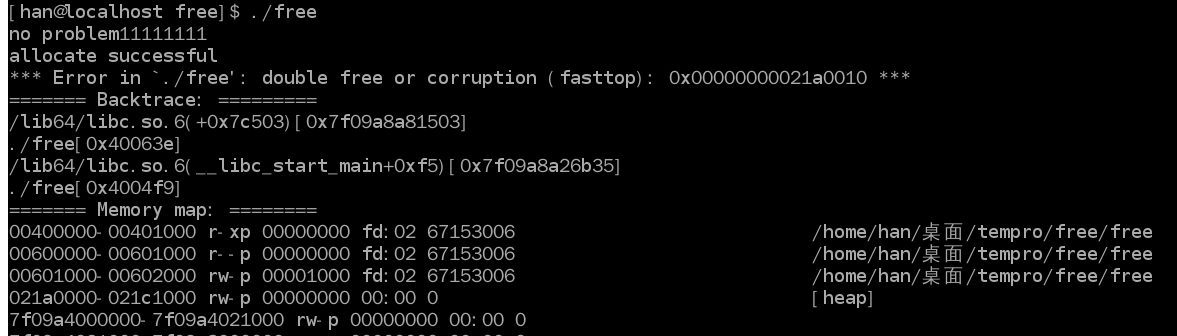
这个程序正好验证了上面的注意事项。
为了避免出现这个错误,自己写了一个函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
void myfree(void ** point){ if(*point != NULL) { free(*point); *point = NULL; }} |
这个函数将一级指针的地址作为菜蔬传入,这样就可以对一级指针进行操作。每次用free释放完空间,都将一级指针置为NULL,这样就避免了重复释放时程序崩溃。
将这个函数应用到刚才的程序中就是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>void myfree(void ** point){ if(*point != NULL) { free(*point); *point = NULL; }}int main(){ char * name = NULL; myfree((void**)&name); myfree((void**)&name); myfree((void**)&name); printf("no problem11111111\n"); name = (char *) malloc(10); if(name) { printf("allocate successful\n"); printf("地址为: %p\n",name); } else { printf("allocate failed\n"); } myfree((void**)&name); myfree((void**)&name); printf("no problem2222222\n"); return 0;} |
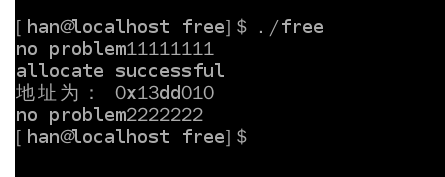
可以发现程序已经没有错误。
但是还有一个问题需要处理: 每次调用myfree函数的时候都需要取一级指针的地址而且需要强制类型转换成void** ,也就是每次都要写(void**)&point,这样很麻烦。
其实我们可以用带参数的宏定义来简化代码,宏定义如下:
|
1
|
#define FREE(p) myfree((void **)&p) |
应用宏定义后的完整代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#define FREE(p) myfree((void **)&p)void myfree(void ** point){ if(*point != NULL) { free(*point); *point = NULL; }}int main(){ char * name = NULL; FREE(name); FREE(name); FREE(name); printf("no problem11111111\n"); name = (char *) malloc(10); if(name) { printf("allocate successful\n"); printf("地址为: %p\n",name); } else { printf("allocate failed\n"); } FREE(name); FREE(name); printf("no problem2222222\n"); return 0;} |
好了今天就写到这里了,希望对你有帮助,如有不正确的地方,还请指点。多谢~~
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/qingergege/p/6550410.html