缘起
最近做遥感影像融合的GWPCA方法,在带宽比较大的时候速度太慢了,需要有个进度条指示一下,然后我去找进度条的库,发现github上面的C/C++的相应的库似乎没有能在VS下跑的,自己花了点时间写了一个。
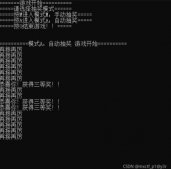
效果

实现
大概需要考虑这样几个要素
- 已完成的百分比
- 执行速度
- 已执行的时间
- 剩余时间
另外进度条的引入不能破坏已有的执行结构,最好和Python的tqdm库类似,通过 start , update 等函数来完成整个进度条,因此对于C语言来说,需要一个定时器,定期将进度条进行重绘(不可能更新一次就重绘一次),因此整个进度条就包含了两个类,一个是进度条类,一个是定时器类。另外需要考虑线程安全的问题。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
|
// Progress.hpp#pragma once#include <ctime>#include <chrono>#include <iostream>#include <iomanip>#include "Timer.hpp"using namespace std::chrono;class ProgressBar{protected: // 进度条的长度(不包含前后缀) unsigned int ncols; // 已完成的数量 std::atomic<unsigned int> finishedNum; // 上次的已完成数量 unsigned int lastNum; // 总数 unsigned int totalNum; // 进度条长度与百分比之间的系数 double colsRatio; // 开始时间 steady_clock::time_point beginTime; // 上次重绘的时间 steady_clock::time_point lastTime; // 重绘周期 milliseconds interval; Timer timer;public: ProgressBar(unsigned int totalNum, milliseconds interval) : totalNum(totalNum), interval(interval), finishedNum(0), lastNum(0), ncols(80), colsRatio(0.8) {} // 开始 void start(); // 完成 void finish(); // 更新 void update() { return this->update(1); } // 一次更新多个数量 void update(unsigned int num) { this->finishedNum += num; } // 获取进度条长度 unsigned int getCols() { return this->ncols; } // 设置进度条长度 void setCols(unsigned int ncols) { this->ncols = ncols; this->colsRatio = ncols / 100; } // 重绘 void show();};void ProgressBar::start() { // 记录开始时间,并初始化定时器 this->beginTime = steady_clock::now(); this->lastTime = this->beginTime; // 定时器用于定时调用重绘函数 this->timer.start(this->interval.count(), std::bind(&ProgressBar::show, this));}// 重绘函数void ProgressBar::show() { // 清除上次的绘制内容 std::cout << "\r"; // 记录重绘的时间点 steady_clock::time_point now = steady_clock::now(); // 获取已完成的数量 unsigned int tmpFinished = this->finishedNum.load(); // 获取与开始时间和上次重绘时间的时间间隔 auto timeFromStart = now - this->beginTime; auto timeFromLast = now - this->lastTime; // 这次完成的数量 unsigned int gap = tmpFinished - this->lastNum; // 计算速度 double rate = gap / duration<double>(timeFromLast).count(); // 应显示的百分数 double present = (100.0 * tmpFinished) / this->totalNum; // 打印百分数 std::cout << std::setprecision(1) << std::fixed << present << "%|"; // 计算应该绘制多少=符号 int barWidth = present * this->colsRatio; // 打印已完成和未完成进度条 std::cout << std::setw(barWidth) << std::setfill('=') << "="; std::cout << std::setw(this->ncols - barWidth) << std::setfill(' ') << "|"; // 打印速度 std::cout << std::setprecision(1) << std::fixed << rate << "op/s|"; // 之后的两部分内容分别为打印已过的时间和剩余时间 int timeFromStartCount = duration<double>(timeFromStart).count(); std::time_t tfs = timeFromStartCount; tm tmfs; gmtime_s(&tmfs, &tfs); std::cout << std::put_time(&tmfs, "%X") << "|"; int timeLast; if (rate != 0) { // 剩余时间的估计是用这次的速度和未完成的数量进行估计 timeLast = (this->totalNum - tmpFinished) / rate; } else { timeLast = INT_MAX; } if ((this->totalNum - tmpFinished) == 0) { timeLast = 0; } std::time_t tl = timeLast; tm tml; gmtime_s(&tml, &tl); std::cout << std::put_time(&tml, "%X"); this->lastNum = tmpFinished; this->lastTime = now;}void ProgressBar::finish() { // 停止定时器 this->timer.stop(); std::cout << std::endl;} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
|
// Timer.hpp#pragma once#include <functional>#include <chrono>#include <thread>#include <atomic>#include <memory>#include <mutex>#include <condition_variable>using namespace std::chrono;class Timer{public: Timer() : _expired(true), _try_to_expire(false) {} Timer(const Timer& timer) { _expired = timer._expired.load(); _try_to_expire = timer._try_to_expire.load(); } ~Timer() { stop(); } void start(int interval, std::function<void()> task) { // is started, do not start again if (_expired == false) return; // start async timer, launch thread and wait in that thread _expired = false; std::thread([this, interval, task]() { while (!_try_to_expire) { // sleep every interval and do the task again and again until times up std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(interval)); task(); } { // timer be stopped, update the condition variable expired and wake main thread std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(_mutex); _expired = true; _expired_cond.notify_one(); } }).detach(); } void startOnce(int delay, std::function<void()> task) { std::thread([delay, task]() { std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(delay)); task(); }).detach(); } void stop() { // do not stop again if (_expired) return; if (_try_to_expire) return; // wait until timer _try_to_expire = true; // change this bool value to make timer while loop stop { std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(_mutex); _expired_cond.wait(locker, [this] {return _expired == true; }); // reset the timer if (_expired == true) _try_to_expire = false; } }private: std::atomic<bool> _expired; // timer stopped status std::atomic<bool> _try_to_expire; // timer is in stop process std::mutex _mutex; std::condition_variable _expired_cond;}; |
定时器类是直接copy了一篇 文章
可以增加的功能
读者可以自行调整一下结构,增加一些有意思的小功能,比如说用于表示完成内容的符号可以替换成大家喜欢的符号,或者加个颜色什么的
还有一些复杂的功能,比如说分组进度条等,不过这个由于我没这方面的需求,因此就没研究了,读者可以自行研究
到此这篇关于用C++实现一个命令行进度条的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ 命令行进度条内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://hkvision.cn/2020/04/09/用c-实现一个命令行进度条/