本文实例为大家分享了C++计算任意权值单源最短路径的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
一、有Dijkstra算法求最短路径了,为什么还要用Bellman-Ford算法
Dijkstra算法不适合用于带有负权值的有向图。
如下图:

用Dijkstra算法求顶点0到各个顶点的最短路径:
(1)首先,把顶点0添加到已访问顶点集合S中,选取权值最小的邻边<0, 2>,权值为5
记录顶点2的最短路径为:dist[2]=5, path[2]=0,把顶点2添加到集合S中。
顶点2,没有邻边(从顶点2出发,其他顶点为终点的边),结束;
(2)访问<0, 1>边,权值为7,把顶点7添加到顶点集合S中,dist[1]=7, path[1]=0。
虽然,顶点1有邻边<1,2>,但是因为顶点2已在集合S中,所以,不继续修改,结束程序。
所以,最终dist[1]=7,dist[2]=5。显然结果不对,顶点2的最短路径应为:0->1->2,权值为7+(-5)=2
二、Bellman-Ford算法思路:
Bellman-Ford算法,效率低,但是适合用于求带有负权值的单源最短路径。
不考虑有回路的,如下图,顶点0到顶点1的最短路径可以无穷小

下面开始简单描述Bellman-Ford的思路:



可以,看到:通过绕过一些顶点,可以取得更短的路径长度
当k=1时,即从源点(顶点0)到其他顶点,只需要一条边。有<0,1>、<0,2>、<0,3>,所以有:dist[1]=6,dist[2]=5,dist[3]=5;
当k=2时,需要2条边的,u=1,有0->2->3,长度为:5+(-2)=3, 更短,所以要修改dist[1]=3;
u=2,有:0->3->2,长度为:5+(-2)=3,更短,所以要修改dist[2]=3;
u=3,没有两条边从顶点0到达顶点3的路径;
u=4,有0->1->4,长度为:6+(-1)=5, 更短,所以要修改dist[4]=5;
u=5,有0->3->5,长度为:5+(-1)=4,更短,所以要修改dist[5]=4;
u=6,没有2条边就可以从顶点0到顶点6的路径。
重复上面步骤,直到k=n-1结束程序。
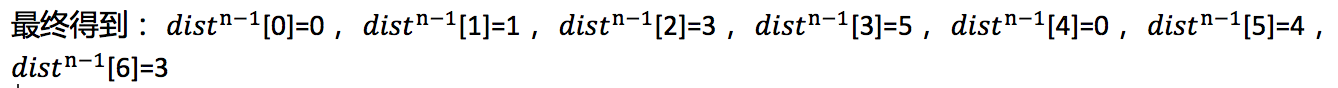
三、实现程序:
1.Graph.h:有向图
- #ifndef Graph_h
- #define Graph_h
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- const int DefaultVertices = 30;
- template <class T, class E>
- struct Edge { // 边结点的定义
- int dest; // 边的另一顶点位置
- E cost; // 表上的权值
- Edge<T, E> *link; // 下一条边链指针
- };
- template <class T, class E>
- struct Vertex { // 顶点的定义
- T data; // 顶点的名字
- Edge<T, E> *adj; // 边链表的头指针
- };
- template <class T, class E>
- class Graphlnk {
- public:
- const E maxValue = 100000; // 代表无穷大的值(=∞)
- Graphlnk(int sz=DefaultVertices); // 构造函数
- ~Graphlnk(); // 析构函数
- void inputGraph(); // 建立邻接表表示的图
- void outputGraph(); // 输出图中的所有顶点和边信息
- T getValue(int i); // 取位置为i的顶点中的值
- E getWeight(int v1, int v2); // 返回边(v1, v2)上的权值
- bool insertVertex(const T& vertex); // 插入顶点
- bool insertEdge(int v1, int v2, E weight); // 插入边
- bool removeVertex(int v); // 删除顶点
- bool removeEdge(int v1, int v2); // 删除边
- int getFirstNeighbor(int v); // 取顶点v的第一个邻接顶点
- int getNextNeighbor(int v,int w); // 取顶点v的邻接顶点w的下一邻接顶点
- int getVertexPos(const T vertex); // 给出顶点vertex在图中的位置
- int numberOfVertices(); // 当前顶点数
- private:
- int maxVertices; // 图中最大的顶点数
- int numEdges; // 当前边数
- int numVertices; // 当前顶点数
- Vertex<T, E> * nodeTable; // 顶点表(各边链表的头结点)
- };
- // 构造函数:建立一个空的邻接表
- template <class T, class E>
- Graphlnk<T, E>::Graphlnk(int sz) {
- maxVertices = sz;
- numVertices = 0;
- numEdges = 0;
- nodeTable = new Vertex<T, E>[maxVertices]; // 创建顶点表数组
- if(nodeTable == NULL) {
- cerr << "存储空间分配错误!" << endl;
- exit(1);
- }
- for(int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++)
- nodeTable[i].adj = NULL;
- }
- // 析构函数
- template <class T, class E>
- Graphlnk<T, E>::~Graphlnk() {
- // 删除各边链表中的结点
- for(int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
- Edge<T, E> *p = nodeTable[i].adj; // 找到其对应链表的首结点
- while(p != NULL) { // 不断地删除第一个结点
- nodeTable[i].adj = p->link;
- delete p;
- p = nodeTable[i].adj;
- }
- }
- delete []nodeTable; // 删除顶点表数组
- }
- // 建立邻接表表示的图
- template <class T, class E>
- void Graphlnk<T, E>::inputGraph() {
- int n, m; // 存储顶点树和边数
- int i, j, k;
- T e1, e2; // 顶点
- E weight; // 边的权值
- cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl;
- cin >> n >> m;
- cout << "请输入各顶点:" << endl;
- for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- cin >> e1;
- insertVertex(e1); // 插入顶点
- }
- cout << "请输入图的各边的信息:" << endl;
- i = 0;
- while(i < m) {
- cin >> e1 >> e2 >> weight;
- j = getVertexPos(e1);
- k = getVertexPos(e2);
- if(j == -1 || k == -1)
- cout << "边两端点信息有误,请重新输入!" << endl;
- else {
- insertEdge(j, k, weight); // 插入边
- i++;
- }
- } // while
- }
- // 输出有向图中的所有顶点和边信息
- template <class T, class E>
- void Graphlnk<T, E>::outputGraph() {
- int n, m, i;
- T e1, e2; // 顶点
- E weight; // 权值
- Edge<T, E> *p;
- n = numVertices;
- m = numEdges;
- cout << "图中的顶点数为" << n << ",边数为" << m << endl;
- for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- p = nodeTable[i].adj;
- while(p != NULL) {
- e1 = getValue(i); // 有向边<i, p->dest>
- e2 = getValue(p->dest);
- weight = p->cost;
- cout << "<" << e1 << ", " << e2 << ", " << weight << ">" << endl;
- p = p->link; // 指向下一个邻接顶点
- }
- }
- }
- // 取位置为i的顶点中的值
- template <class T, class E>
- T Graphlnk<T, E>::getValue(int i) {
- if(i >= 0 && i < numVertices)
- return nodeTable[i].data;
- return NULL;
- }
- // 返回边(v1, v2)上的权值
- template <class T, class E>
- E Graphlnk<T, E>::getWeight(int v1, int v2) {
- if(v1 != -1 && v2 != -1) {
- if(v1 == v2) // 说明是同一顶点
- return 0;
- Edge<T , E> *p = nodeTable[v1].adj; // v1的第一条关联的边
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != v2) { // 寻找邻接顶点v2
- p = p->link;
- }
- if(p != NULL)
- return p->cost;
- }
- return maxValue; // 边(v1, v2)不存在,就存放无穷大的值
- }
- // 插入顶点
- template <class T, class E>
- bool Graphlnk<T, E>::insertVertex(const T& vertex) {
- if(numVertices == maxVertices) // 顶点表满,不能插入
- return false;
- nodeTable[numVertices].data = vertex; // 插入在表的最后
- numVertices++;
- return true;
- }
- // 插入边
- template <class T, class E>
- bool Graphlnk<T, E>::insertEdge(int v1, int v2, E weight) {
- if(v1 == v2) // 同一顶点不插入
- return false;
- if(v1 >= 0 && v1 < numVertices && v2 >= 0 && v2 < numVertices) {
- Edge<T, E> *p = nodeTable[v1].adj; // v1对应的边链表头指针
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != v2) // 寻找邻接顶点v2
- p = p->link;
- if(p != NULL) // 已存在该边,不插入
- return false;
- p = new Edge<T, E>; // 创建新结点
- p->dest = v2;
- p->cost = weight;
- p->link = nodeTable[v1].adj; // 链入v1边链表
- nodeTable[v1].adj = p;
- numEdges++;
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- // 有向图删除顶点较麻烦
- template <class T, class E>
- bool Graphlnk<T, E>::removeVertex(int v) {
- if(numVertices == 1 || v < 0 || v > numVertices)
- return false; // 表空或顶点号超出范围
- Edge<T, E> *p, *s;
- // 1.清除顶点v的边链表结点w 边<v,w>
- while(nodeTable[v].adj != NULL) {
- p = nodeTable[v].adj;
- nodeTable[v].adj = p->link;
- delete p;
- numEdges--; // 与顶点v相关联的边数减1
- } // while结束
- // 2.清除<w, v>,与v有关的边
- for(int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
- if(i != v) { // 不是当前顶点v
- s = NULL;
- p = nodeTable[i].adj;
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != v) {// 在顶点i的链表中找v的顶点
- s = p;
- p = p->link; // 往后找
- }
- if(p != NULL) { // 找到了v的结点
- if(s == NULL) { // 说明p是nodeTable[i].adj
- nodeTable[i].adj = p->link;
- } else {
- s->link = p->link; // 保存p的下一个顶点信息
- }
- delete p; // 删除结点p
- numEdges--; // 与顶点v相关联的边数减1
- }
- }
- }
- numVertices--; // 图的顶点个数减1
- nodeTable[v].data = nodeTable[numVertices].data; // 填补,此时numVertices,比原来numVertices小1,所以,这里不需要numVertices-1
- nodeTable[v].adj = nodeTable[numVertices].adj;
- // 3.要将填补的顶点对应的位置改写
- for(int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
- p = nodeTable[i].adj;
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != numVertices) // 在顶点i的链表中找numVertices的顶点
- p = p->link; // 往后找
- if(p != NULL) // 找到了numVertices的结点
- p->dest = v; // 将邻接顶点numVertices改成v
- }
- return true;
- }
- // 删除边
- template <class T, class E>
- bool Graphlnk<T, E>::removeEdge(int v1, int v2) {
- if(v1 != -1 && v2 != -1) {
- Edge<T, E> * p = nodeTable[v1].adj, *q = NULL;
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != v2) { // v1对应边链表中找被删除边
- q = p;
- p = p->link;
- }
- if(p != NULL) { // 找到被删除边结点
- if(q == NULL) // 删除的结点是边链表的首结点
- nodeTable[v1].adj = p->link;
- else
- q->link = p->link; // 不是,重新链接
- delete p;
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false; // 没有找到结点
- }
- // 取顶点v的第一个邻接顶点
- template <class T, class E>
- int Graphlnk<T, E>::getFirstNeighbor(int v) {
- if(v != -1) {
- Edge<T, E> *p = nodeTable[v].adj; // 对应链表第一个边结点
- if(p != NULL) // 存在,返回第一个邻接顶点
- return p->dest;
- }
- return -1; // 第一个邻接顶点不存在
- }
- // 取顶点v的邻接顶点w的下一邻接顶点
- template <class T, class E>
- int Graphlnk<T, E>::getNextNeighbor(int v,int w) {
- if(v != -1) {
- Edge<T, E> *p = nodeTable[v].adj; // 对应链表第一个边结点
- while(p != NULL && p->dest != w) // 寻找邻接顶点w
- p = p->link;
- if(p != NULL && p->link != NULL)
- return p->link->dest; // 返回下一个邻接顶点
- }
- return -1; // 下一个邻接顶点不存在
- }
- // 给出顶点vertex在图中的位置
- template <class T, class E>
- int Graphlnk<T, E>::getVertexPos(const T vertex) {
- for(int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
- if(nodeTable[i].data == vertex)
- return i;
- return -1;
- }
- // 当前顶点数
- template <class T, class E>
- int Graphlnk<T, E>::numberOfVertices() {
- return numVertices;
- }
- #endif /* Graph_h */
2.Bellman-Ford.h
- #ifndef Bellman_Ford_h
- #define Bellman_Ford_h
- #include "Graph.h"
- // Bellman-Ford算法
- template<class T, class E>
- void BellmanFord(Graphlnk<T, E> &G, int v, E dist[], int path[]) {
- int i, k, u, n = G.numberOfVertices();
- E w;
- // 1.初始化,将顶点v作为u顶点(存在<v, u>有向边)的上一个顶点,记录路径
- for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- dist[i] = G.getWeight(v, i);
- if(i != v && dist[i] < G.maxValue)
- path[i] = v;
- else
- path[i] = -1;
- }
- // 2.迭代求解:反复对边集E中的每条边进行松弛操作,使得顶点集V中的每个顶点的最短距离估计值逐步逼近其最短距离;(运行n-1次,因为上面算是1次:k=1,所以,k从2开始)
- bool isFlag; // 监视该轮dist数组是否有变化
- for(k = 2; k < n; k++) {
- isFlag = false;
- for(u = 0; u < n; u++) { // 遍历顶点,找不是v的顶点
- if(u != v) {
- for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- w = G.getWeight(i, u);
- if(w != 0 && w < G.maxValue && dist[u] > dist[i] + w) {
- // 存在<i, u>边,并且绕过i,使得路径更短,就修改u顶点的最短路径
- // w可能是负权值,如果i和u是同一顶点,则w是0,排除同一顶点的情况
- // 也可以不写w!=0,因为同一顶点,w=0,dist[u]==dist[i]+w会不满足
- // dist[u] > dist[i] + w这个条件
- dist[u] = dist[i] + w;
- path[u] = i; // 记忆路径
- isFlag = true;
- }
- } // 第3重循环
- }
- } // 第2重循环
- if(isFlag == false) // 如果dist数组没有变化,说明各个顶点已求得最短路径
- break;
- } // 第1重for循环
- }
- // 从path数组读取最短路径的算法
- template <class T, class E>
- void printShortestPath(Graphlnk<T, E> &G, int v, E dist[], int path[]) {
- int i, j, k, n = G.numberOfVertices();
- int *d = new int[n];
- cout << "从顶点" << G.getValue(v) << "到其他各顶点的最短路径为:" << endl;
- for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if(i != v) { // 如果不是顶点v
- j = i;
- k = 0;
- while(j != v) {
- d[k++] = j;
- j = path[j];
- }
- cout << "顶点" << G.getValue(i) << "的最短路径为:" << G.getValue(v);
- while(k > 0)
- cout << "->" << G.getValue(d[--k]);
- cout << ",最短路径长度为:" << dist[i] << endl;
- }
- }
- }
- #endif /* Bellman_Ford_h */
3.main.cpp
- /*
- 测试数据:
- 7 10
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 0 1 6
- 0 2 5
- 0 3 5
- 1 4 -1
- 2 1 -2
- 2 4 1
- 3 2 -2
- 3 5 -1
- 4 6 3
- 5 6 3
- */
- #include "Bellman-Ford.h"
- const int maxSize = 40;
- int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
- Graphlnk<char, int> G; // 声明图对象
- int dist[maxSize], path[maxSize], v;
- char u0;
- // 创建图
- G.inputGraph();
- cout << "图的信息如下:" << endl;
- G.outputGraph();
- cout << "请输入起始顶点u0:" << endl;
- cin >> u0;
- v = G.getVertexPos(u0); // 取得起始顶点的位置
- // 我把dist数组放到有向图头文件中,方便建立有向图时,同时初始化dist数组
- BellmanFord(G, v, dist, path); // 调用BellmanFord函数
- printShortestPath(G, v, dist, path); // 输出到各个顶点的最短路径
- return 0;
- }
测试结果:

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/chuanzhouxiao/article/details/88876704