一、常见内置模块
1.1什么叫做模块?
import XXXX
xxxxx就是模块 .py
1.2模块的分类
1.random
2.math
3.内置模块
1.3第三方的模块(需要安装)
在线安装 cmd 窗口下通过 pip install 模块名
python -m pip install 模块的名
离线安装 下载好所需要的安装包 zip ---- 解压安装包 ------setup.py--------cmd : python install
setup.py
二、模块导入的问题
import 模块名
import random
import 模块名 as 别名
import random as r
from 包 import 模块的名称
from os import path
三、random模块
用来产生随机数(伪随机数)
[ ‘BPF", ‘LOG4", ‘NV_MAGICCONST", ‘RECIP_BPF", ‘Random", ‘SG_MAGICCONST", ‘SystemRandom",‘TWOPI", ‘Sequence", ‘Set", ‘all", ‘builtins", ‘cached", ‘doc", ‘file", ‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec",‘accumulate", ‘acos", ‘bisect", ‘ceil", ‘cos", ‘e", ‘exp", ‘floor", ‘inst", ‘log", ‘os", ‘pi", ‘random", ‘repeat", ‘sha512",‘sin", ‘sqrt", ‘test", ‘test_generator", ‘urandom", ‘_warn", ‘betavariate", ‘choice", ‘choices", ‘expovariate",‘gammavariate", ‘gauss", ‘getrandbits", ‘getstate", ‘lognormvariate", ‘normalvariate", ‘paretovariate",‘randbytes", ‘randint", ‘random", ‘randrange", ‘sample", ‘seed", ‘setstate", ‘shuffle", ‘triangular",‘uniform", ‘vonmisesvariate", ‘weibullvariate" ]
主要常见的random模块的函数:
3.1randint() --------- 产生随机整数[m,n]
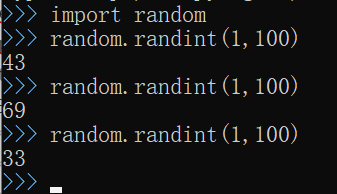
3.2random() --------------产生0-1的随机数[0,1)
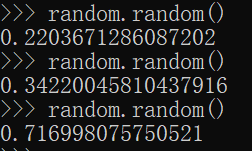
3.3uniform() ------------- 产生正态分布的随机数
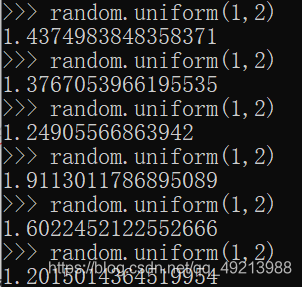
3.4randrange() ------ 产生一个范围内的随机数

3.5choices() ---------- 用在序列(容器)(有序的序列)随机筛取一个元素

四、math模块
用于数学运算
[‘doc", ‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec", ‘acos", ‘acosh", ‘asin", ‘asinh", ‘atan", ‘atan2", ‘atanh",
‘ceil", ‘comb", ‘copysign", ‘cos", ‘cosh", ‘degrees", ‘dist", ‘e", ‘erf", ‘erfc", ‘exp", ‘expm1", ‘fabs", ‘factorial",
‘floor", ‘fmod", ‘frexp", ‘fsum", ‘gamma", ‘gcd", ‘hypot", ‘inf", ‘isclose", ‘isfinite", ‘isinf", ‘isnan", ‘isqrt",
‘lcm", ‘ldexp", ‘lgamma", ‘log", ‘log10", ‘log1p", ‘log2", ‘modf", ‘nan", ‘nextafter", ‘perm", ‘pi", ‘pow",
‘prod", ‘radians", ‘remainder", ‘sin", ‘sinh", ‘sqrt", ‘tan", ‘tanh", ‘tau", ‘trunc", ‘ulp"]
ceil ------------- 向上取整
floor ----------- 向下取整
e ------------ 属性 自然常数
fabs ----------- 求绝对值 等价 abs() 全局函数
fmod ----------- 求模运算
isnan -------- 判断是不是数字 (是数字返回 false nan -----not a number)
isfinite ----- 判断是不是无限
pi ----------- 圆周率
pow ------------- 幂次方
sqrt ---------- 平方根
五、os模块
5.1操作系统文件
清屏的方法 --------- import os os.system(“cls”)
[‘DirEntry", ‘F_OK", ‘GenericAlias", ‘Mapping", ‘MutableMapping", ‘O_APPEND", ‘O_BINARY",
‘O_CREAT", ‘O_EXCL", ‘O_NOINHERIT", ‘O_RANDOM", ‘O_RDONLY", ‘O_RDWR", ‘O_SEQUENTIAL",
‘O_SHORT_LIVED", ‘O_TEMPORARY", ‘O_TEXT", ‘O_TRUNC", ‘O_WRONLY", ‘P_DETACH", ‘P_NOWAIT",‘P_NOWAITO", ‘P_OVERLAY", ‘P_WAIT", ‘PathLike", ‘R_OK", ‘SEEK_CUR", ‘SEEK_END", ‘SEEK_SET",‘TMP_MAX", ‘W_OK", ‘X_OK", ‘AddedDllDirectory", ‘Environ", ‘all", ‘builtins", ‘cached", ‘doc", ‘file",‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec", ‘check_methods", ‘execvpe", ‘exists", ‘exit", ‘fspath",
‘get_exports_list", ‘walk", ‘wrap_close", ‘abc", ‘abort", ‘access", ‘add_dll_directory", ‘altsep", ‘chdir",
‘chmod", ‘close", ‘closerange", ‘cpu_count", ‘curdir", ‘defpath", ‘device_encoding", ‘devnull", ‘dup",
‘dup2", ‘environ", ‘error", ‘execl", ‘execle", ‘execlp", ‘execlpe", ‘execv", ‘execve", ‘execvp", ‘execvpe",
‘extsep", ‘fdopen", ‘fsdecode", ‘fsencode", ‘fspath", ‘fstat", ‘fsync", ‘ftruncate", ‘get_exec_path",
‘get_handle_inheritable", ‘get_inheritable", ‘get_terminal_size", ‘getcwd", ‘getcwdb", ‘getenv",
‘getlogin", ‘getpid", ‘getppid", ‘isatty", ‘kill", ‘linesep", ‘link", ‘listdir", ‘lseek", ‘lstat", ‘makedirs", ‘mkdir",
‘name", ‘open", ‘pardir", ‘path", ‘pathsep", ‘pipe", ‘popen", ‘putenv", ‘read", ‘readlink", ‘remove",
‘removedirs", ‘rename", ‘renames", ‘replace", ‘rmdir", ‘scandir", ‘sep", ‘set_handle_inheritable",
‘set_inheritable", ‘spawnl", ‘spawnle", ‘spawnv", ‘spawnve", ‘st", ‘startfile", ‘stat", ‘stat_result",
‘statvfs_result", ‘strerror", ‘supports_bytes_environ", ‘supports_dir_fd", ‘supports_effective_ids",
‘supports_fd", ‘supports_follow_symlinks", ‘symlink", ‘sys", ‘system", ‘terminal_size", ‘times",
‘times_result", ‘truncate", ‘umask", ‘uname_result", ‘unlink", ‘unsetenv", ‘urandom", ‘utime", ‘waitpid",
‘waitstatus_to_exitcode", ‘walk", ‘write"]
5.2os模块常用方法
chdir() ------- 修改工作目录
curdir ------- 获取当前的目录 返回的结果的是相对路径 (绝对路径 os.path.abspath(os.curdir) )
chmod() ---------修改权限
close -------- 关闭文件的路径
cpu_count() --------- 返回的cpu的核对应得线程数
getcwd() ----------获取当前路径,返回得是绝对路径,相当linux下pwd
getpid()-------获取当前进程的进程编号
getppid() ------------获取当前进程的父进程的进程编号
kill() ------------- 通过进程编号杀死进程
linesep -------- 属性 对应系统下的换行符
listdir() ------ 返回的对应目录下所有的文件和文件夹(隐藏的文件夹),返回的是列表
makedirs() ----- 创建目录,支持多层目录的创建
mkdir() ----- 创建目录,只能创建一层,不支持多层
open()------创建文件 open()全局函数
pathsep ------- 获取环境变量分隔符 windows ; linux分割符 :
sep --------- 获取路径分割符
remove(文件名或者路径) ----------删除文件
removedirs() --------------- 删除目录,支持多级删除(递归)
system()-------- 执行终端命令
5.3os.path模块
import os.path import os.path as p from os import path
[‘all", ‘builtins", ‘cached", ‘doc", ‘file", ‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec", ‘abspath_fallback",
‘get_bothseps", ‘getfinalpathname", ‘getfinalpathname_nonstrict", ‘getfullpathname",
‘getvolumepathname", ‘nt_readlink", ‘readlink_deep", ‘abspath", ‘altsep", ‘basename", ‘commonpath",
‘commonprefix", ‘curdir", ‘defpath", ‘devnull", ‘dirname", ‘exists", ‘expanduser", ‘expandvars", ‘extsep",
‘genericpath", ‘getatime", ‘getctime", ‘getmtime", ‘getsize", ‘isabs", ‘isdir", ‘isfile", ‘islink", ‘ismount",
‘join", ‘lexists", ‘normcase", ‘normpath", ‘os", ‘pardir", ‘pathsep", ‘realpath", ‘relpath", ‘samefile",
‘sameopenfile", ‘samestat", ‘sep", ‘split", ‘splitdrive", ‘splitext", ‘stat", ‘supports_unicode_filenames",
‘sys"]
abspath(相对路径) ----------------- 返回的路径的所对应的绝对路径
altsep ------------------ 返回的python中的分隔符
basename ------------ 文件名称
dirname ----------- 文件目录
exists ---------------- 判断文件或者目录是否存在
getctime -------- 获取时间(创建时间)
getmtime ------------ 获取修改时间
getsize ------------ 获取文件的大小,单位是字节
isdir-------------- 判断path是否是目录(文件夹)
isfile-------------------判断path是否是文件
isabs ------------- 判断是不是绝对路径
islink ------- 判断是不是链接
ismount ---------- 判断是不是挂载文件
join -------------- 拼接路径
sep ----------- 路径分隔符
split ----------分割路径
relpath ------------- 返回的真正的路径和abspath一样
5.4练习
需要结合os.path 和 os 模块,以及函数的递归
给出一个路径,遍历当前路径所有文件和文件夹,打印出所有的文件(遇到文件输出路径,如果遇
到的文件夹继续遍历文件夹)
import os
from os import path
def scanner_file(url):
files = os.listdir(url)
#拼接路径
for file in files:
#real_path = url + "" + f
real_path = path.join(url,file)
#print (file)
if path.isfile(real_path):
l = path.abspath(real_path) # 把取出来的路径赋值给L
print(l)#输出在屏幕上
elif path.isdir(real_path):
scanner_file(real_path)
else:
print("其他情况")
pass
scanner_file("E:")
六、sys模块
[‘breakpointhook", ‘displayhook", ‘doc", ‘excepthook", ‘interactivehook", ‘loader", ‘name",
‘package", ‘spec", ‘stderr", ‘stdin", ‘stdout", ‘unraisablehook", ‘base_executable", ‘clear_type_cache",
‘current_frames", ‘debugmallocstats", ‘enablelegacywindowsfsencoding", ‘framework", ‘getframe", ‘git",
‘home", ‘xoptions", ‘addaudithook", ‘api_version", ‘argv", ‘audit", ‘base_exec_prefix", ‘base_prefix",
‘breakpointhook", ‘builtin_module_names", ‘byteorder", ‘call_tracing", ‘copyright", ‘displayhook",
‘dllhandle", ‘dont_write_bytecode", ‘exc_info", ‘excepthook", ‘exec_prefix", ‘executable", ‘exit", ‘flags",
‘float_info", ‘float_repr_style", ‘get_asyncgen_hooks", ‘get_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth",
‘getallocatedblocks", ‘getdefaultencoding", ‘getfilesystemencodeerrors", ‘getfilesystemencoding",
‘getprofile", ‘getrecursionlimit", ‘getrefcount", ‘getsizeof", ‘getswitchinterval", ‘gettrace",
‘getwindowsversion", ‘hash_info", ‘hexversion", ‘implementation", ‘int_info", ‘intern", ‘is_finalizing",
‘maxsize", ‘maxunicode", ‘meta_path", ‘modules", ‘path", ‘path_hooks", ‘path_importer_cache",
‘platform", ‘platlibdir", ‘prefix", ‘ps1", ‘ps2", ‘pycache_prefix", ‘set_asyncgen_hooks"
‘set_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth", ‘setprofile", ‘setrecursionlimit", ‘setswitchinterval", ‘settrace",
‘stderr", ‘stdin", ‘stdout", ‘thread_info", ‘unraisablehook", ‘version", ‘version_info", ‘warnoptions",
‘winver"]
api_version -------------- 属性 获取python内部的版本号
argv --------- 接收脚本参数
copyright ------------ 输出cpython版本号
exit ---------- 退出系统
getdefaultencoding()-------------获取的默认编码,python3默认编码是utf-8
getfilesystemencoding()------------ 获取文件系统的默认编程,默认utf-8
getrecursionlimit()------- 获取python对递归的限制层数
setrecursionlimit() -------------重新设置递归的限制的层数
getrefcount(对象)--------- 获取对象的引用计数,是垃圾回收机制里的引用计数,注意任何对象都
有一个默认引用计数
getwindowsversion() ---------- 获取当前窗口的版本信息
version -----------## 标题-- 获取版本信息
**python的垃圾回收机制:
以引用计数为主,以标记清除和分代收集为辅
Java 以标记清除为主,以引用计数和分代收集为辅 **
七、时间模块
7.1time模块
python提供操作日期和时间的模块
["_STRUCT_TM_ITEMS", ‘doc", ‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec", ‘altzone", ‘asctime", ‘ctime",
‘daylight", ‘get_clock_info", ‘gmtime", ‘localtime", ‘mktime", ‘monotonic", ‘monotonic_ns",
‘perf_counter", ‘perf_counter_ns", ‘process_time", ‘process_time_ns", ‘sleep", ‘strftime", ‘strptime",
‘struct_time", ‘thread_time", ‘thread_time_ns", ‘time", ‘time_ns", ‘timezone", ‘tzname"]
asctime() ------------ 获取当前时间
ctime()------ 获取当前时间
localtime()------ 获取的本地时间,返回的是对象
sleep()-------- 表示休眠的时间,单位秒
time()---------------- 获取当前系统的时间戳,单位也是秒
strftime()------- 将时间对象格式化成字符串
strptime()------将一个特定的时间字符串转换为时间对象
7.2datetime模块
对Time模块的补充
from datetime import datetime
[‘add", ‘class", ‘delattr", ‘dir", ‘doc", ‘eq", ‘format", ‘ge", ‘getattribute", ‘gt", ‘hash", ‘init",
‘init_subclass", ‘le", ‘lt", ‘ne", ‘new", ‘radd", ‘reduce", ‘reduce_ex", ‘repr", ‘rsub", ‘setattr", ‘sizeof",
‘str", ‘sub", ‘subclasshook", ‘astimezone", ‘combine", ‘ctime", ‘date", ‘day", ‘dst", ‘fold",
‘fromisocalendar", ‘fromisoformat", ‘fromordinal", ‘fromtimestamp", ‘hour", ‘isocalendar",
‘isoformat", ‘isoweekday", ‘max", ‘microsecond", ‘min", ‘minute", ‘month", ‘now", ‘replace", ‘resolution",
‘second", ‘strftime", ‘strptime", ‘time", ‘timestamp", ‘timetuple", ‘timetz", ‘today", ‘toordinal", ‘tzinfo",
‘tzname", ‘utcfromtimestamp", ‘utcnow", ‘utcoffset", ‘utctimetuple", ‘weekday", ‘year"]
now() ------------获取当前的时间
八、其他模块
日历的模块(calendar)
uuid 模块 ------------ 一般会用在文件上传或者文件备份的时候:
产生一个永不重复的字符串
uuid.uuid4().hex
练习:完成用户注册登录的案例(加盐值混淆)
import sys
import hashlib
users=[]
salt = "#!@$@!%^#&^!&!##@!"
def main():
print("*~"*20)
print("1.用户注册")
print("2.用户登录")
print("3.退出系统")
print("*~"*20)
choice = input("请选择对应想要的操作:")
return choice
def register():
username = input("请输入注册用户名:")
passwd = input("请输入注册用户密码:")
if username == None or username.strip() == "":
print("用户名不能为空")
return
if passwd == None or passwd.strip()=="" or len(passwd) < 6:
print("用户密码不能为空或者小于6位长度")
return
passwd = passwd_md5(passwd)
for i in users:
if i.get("username") == username:
print("用户名重复")
return
user = {}
user["username"] = username
user["passwd"] = passwd
users.append(user)
print(users)
def passwd_md5(passwd):
md5 = hashlib.md5(passwd.encode("utf-8"))
md5.update(salt.encode("utf-8"))
return md5.hexdigest()
def is_login(username,passwd):
for i in users:
if i.get("username") == username and i.get("passwd") == passwd:
return True
return False
def login():
username = input("请输入登陆的用户名:")
passwd = input("请输入登陆用户密码:")
passwd = passwd_md5(passwd)
if is_login(username,passwd):
print("恭喜,登陆成功")
print(users) /
else:
print("抱歉,登陆失败")
while(True):
choice = main()
if choice == "1":
print("注册")
register()
elif choice =="2":
print("登陆")
login()
elif choice =="3":
print("退出系统......")
sys.exit()
九、加密算法的介绍
有了解加密? 加密是计算机中最重要的技术之一
分类:
以算法的是否可逆:
| 可逆算法 |
是不是使用同一密钥:
对称加密
| 解密和加密的时候使用同一个密钥 |
| DES算法 |
不对称加密
加密和解密使用的是同一对密钥(公钥、私钥)https协议 RSA算法
不可逆算法(hash算法)
特点:不可逆、结果是唯一的
MD5
十、hashlib库
10.1哈希算法
import hashlib
使用步骤:
创建算法对象(md5 sha256),返回的是算法对象
md5 = hashlib.md5()
md5
一个字符串加密的话md5 = hashlib.md5(“123”.encode(“utf-8”))
如果不做盐值混淆, md5.hexdigest()
盐值混淆
md5.update(盐值)
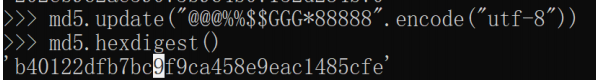
盐值越复杂,加密的安全性就越高
cmd5.com 解密
10.2hmac库
也是一个哈希加密库,用到了对称加密
new()
参数:第一个参数是要加密的字符串,第二个参数盐值,第三个参数是加密算法
首先使用对称加密(密钥就是盐值),得到加密的结果之后又进行了一次hash加密(盐值混淆)

十一、对象序列化
什么是对象序列化?
字典 列表 元组 集合 -------------- 对象
序列化:将抽象的这些对象的概念转换真正的字符或者字节数据
十二、pickle模块
[‘ADDITEMS", ‘APPEND", ‘APPENDS", ‘BINBYTES", ‘BINBYTES8", ‘BINFLOAT", ‘BINGET", ‘BININT",
‘BININT1", ‘BININT2", ‘BINPERSID", ‘BINPUT", ‘BINSTRING", ‘BINUNICODE", ‘BINUNICODE8", ‘BUILD",‘BYTEARRAY8", ‘DEFAULT_PROTOCOL", ‘DICT", ‘DUP", ‘EMPTY_DICT", ‘EMPTY_LIST", ‘EMPTY_SET",‘EMPTY_TUPLE", ‘EXT1", ‘EXT2", ‘EXT4", ‘FALSE", ‘FLOAT", ‘FRAME", ‘FROZENSET", ‘FunctionType", ‘GET",‘GLOBAL", ‘HIGHEST_PROTOCOL", ‘INST", ‘INT", ‘LIST", ‘LONG", ‘LONG1", ‘LONG4", ‘LONG_BINGET",‘LONG_BINPUT", ‘MARK", ‘MEMOIZE", ‘NEWFALSE", ‘NEWOBJ", ‘NEWOBJ_EX", ‘NEWTRUE",‘NEXT_BUFFER", ‘NONE", ‘OBJ", ‘PERSID", ‘POP", ‘POP_MARK", ‘PROTO", ‘PUT", ‘PickleBuffer",‘PickleError", ‘Pickler", ‘PicklingError", ‘PyStringMap", ‘READONLY_BUFFER", ‘REDUCE", ‘SETITEM",‘SETITEMS", ‘SHORT_BINBYTES", ‘SHORT_BINSTRING", ‘SHORT_BINUNICODE", ‘STACK_GLOBAL",‘STOP", ‘STRING", ‘TRUE", ‘TUPLE", ‘TUPLE1", ‘TUPLE2", ‘TUPLE3", ‘UNICODE", ‘Unpickler",‘UnpicklingError", ‘Framer", ‘HAVE_PICKLE_BUFFER", ‘Pickler", ‘Stop", ‘Unframer", ‘Unpickler", ‘all",‘builtins", ‘cached", ‘doc", ‘file", ‘loader", ‘name", ‘package", ‘spec", ‘compat_pickle", ‘dump", ‘dumps",‘extension_cache", ‘extension_registry", ‘getattribute", ‘inverted_registry", ‘load", ‘loads", ‘test",
‘_tuplesize2code", ‘bytes_types", ‘codecs", ‘compatible_formats", ‘decode_long", ‘dispatch_table",
‘dump", ‘dumps", ‘encode_long", ‘format_version", ‘io", ‘islice", ‘load", ‘loads", ‘maxsize", ‘pack",
‘partial", ‘re", ‘sys", ‘unpack", ‘whichmodule"]
dumps -------------- 将对象序列化为字节数据 .dat
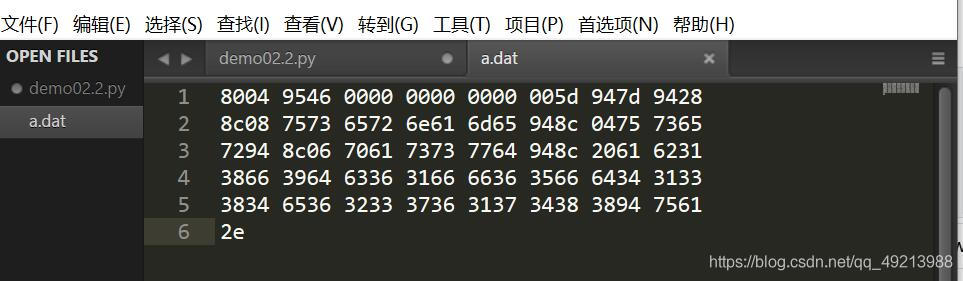
loads -------------- 将数据反序列化为对象
users = [1,2,3,4,5]
data = pickle.dumps(users) # 将对象序列化
f = open("a.txt","wb")
f.write(data)
f.close()
f = open("a.dat","wb")
f.write(data)
f.close()
f = open("a.dat","rb")
show = f.read()
print(data,"
")
print("对象序列化为字节数据:",show,"
")
print("将数据反序列化为对象:",pickle.loads(show),"
") #将数据反序列化为对象
dump --------------将对象序列化为字节数据 ,并且保存到file
load -------------- 将数据反序列化为对象
十三、json模块
Python2只能操作字典对象
dumps -------------- 将对象序列化为字节数据 .dat
loads -------------- 将数据反序列化为对象
dump --------------将对象序列化为字节数据 ,并且保存到file
load -------------- 将数据反序列化为对象
到此这篇关于python常见模块与用法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python模块用法内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_49213988/article/details/115696782