本文实例为大家分享了C语言实现BST二叉排序树的基本操作代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
BST-二叉排序树的几个基本操作。
头文件声明与函数定义
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElemType;/*** 定义节点*/typedef struct BSTNode{ ElemType data;//数据域 struct BSTNode *lchild,//左孩子 *rchild;//右孩子}BSTNode;/*** 插入节点*/int BST_InsertNode(BSTNode** bstNode,ElemType e);/*** 创建BST树*/void BST_Create(BSTNode** bstTree,ElemType* dataSet,int n);/** * 查找BST树节点 */BSTNode* BST_SearchNode(BSTNode** bstNode,ElemType e);/** * 遍历BST树节点 */void BST_PrintNodes(BSTNode* bstNode); |
函数编写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
#include "BSTree.h"/*** 插入节点*/int BST_InsertNode(BSTNode** bstNode,ElemType e){ //如果BST树为空,直接创建根节点 if (*bstNode==NULL) { *bstNode=(BSTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode)); (*bstNode)->data=e; (*bstNode)->lchild=NULL; (*bstNode)->rchild=NULL; return 1; } //如果BST树不为空,则比较插入值与根节点值的大小关系 if ((*bstNode)->data==e) return 0;//关键值相同,则插入失败 else if ((*bstNode)->data>e) return BST_InsertNode(&(*bstNode)->lchild,e);//大于插入值,将其作为左子树节点 else if ((*bstNode)->data<e) return BST_InsertNode(&(*bstNode)->rchild,e);//小于插入值,将其作为右子树节点}/*** 创建BST树*/void BST_Create(BSTNode** bstTree,ElemType* dataSet,int n){ int i=0; *bstTree=NULL;//BST树初始化为空 while (i<n) { printf("%d\t",dataSet[i]); BST_InsertNode(bstTree,dataSet[i++]); } printf("\n");}/** * 查找BST树节点 */BSTNode* BST_SearchNode(BSTNode** bstNode,ElemType e){ if (*bstNode==NULL)//判空 return *bstNode; //查找结点 if ((*bstNode)->data==e)//验证是否为根节点 return *bstNode; else if ((*bstNode)->data>e) { return BST_SearchNode(&(*bstNode)->lchild,e);//如果小于根节点的值,查找左子树 }else { return BST_SearchNode(&(*bstNode)->rchild,e);//如果大于根节点的值,查找右子树 }}/** * 遍历BST树节点 */void BST_PrintNodes(BSTNode* bstNode){ if (bstNode==NULL)//根节点判空 { return; } //打印根节点的值 printf("%d\t",(bstNode)->data); //从根节点开始遍历 if (bstNode->lchild!=NULL) BST_PrintNodes((bstNode)->lchild);//遍历左子树 if (bstNode->rchild!=NULL) BST_PrintNodes(bstNode->rchild);//遍历右子树} |
测试
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#include "BSTree.h"int main(int argc,char** argv){ int i; ElemType arr[]={45,24,53,45,12,24,68,25,36,96,100,25,64,78};//只有4个元素,因为关键字重复的元素不能被插入 BSTNode* bstNode=NULL; BSTNode* bstTemp=NULL; //创建BST树 BST_Create(&bstNode,arr,sizeof(arr)/sizeof(ElemType)); printf("%d\t%d\n",bstNode,bstNode->data); printf("%d\t%d\n",bstNode,bstNode->lchild->data); //查找结点 bstTemp=BST_SearchNode(&bstNode,53); printf("the aimed node is %d,\n",bstNode->data); //遍历BST树的所有节点 BST_PrintNodes(bstNode); printf("\n");} |
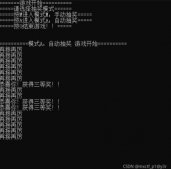
贴上测试结果如下,【插入和遍历的节点数量不一致是因为-如果BST树中的节点关键值相同,就终止插入操作】

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43524214/article/details/120320678