最近在使用Testlink时,发现导入的用例是xml格式,且没有合适的工具转成excel格式,xml使用excel打开显示的东西也太多,网上也有相关工具转成csv格式的,结果也不合人意。
那求人不如尔己,自己写一个吧
需要用到的模块有:xml.dom.minidom(python自带)、xlwt
使用版本:
python:2.7.5
xlwt:1.0.0
一、先分析Testlink XML格式:
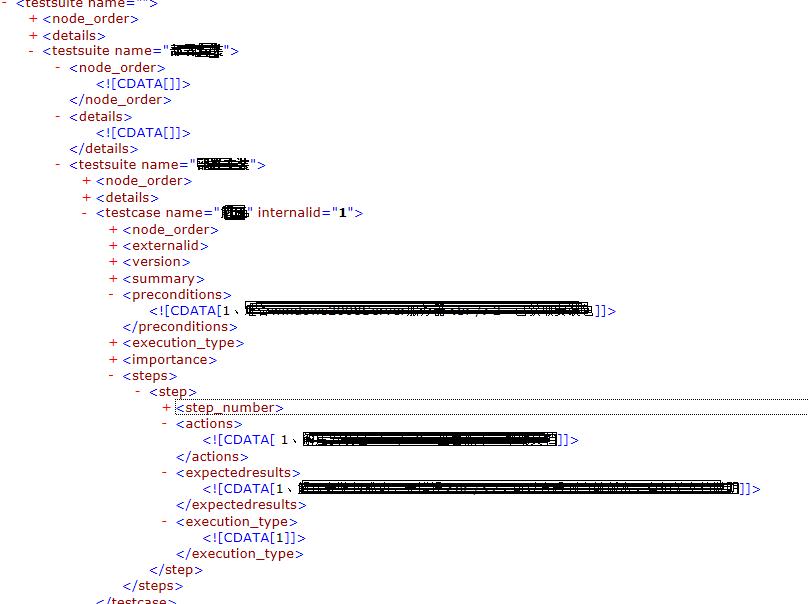
这是一个有两级testusuit的典型的testlink用例结构,我们只需要取testsuite name,testcase name,preconditions,actions,expectedresults
二、程序如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
#coding:utf-8'''Created on 2015-8-20@author: Administrator'''''''''import xml.etree.cElementTree as ETimport xml.dom.minidom as xximport os,xlwt,datetimeworkbook=xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8")# booksheet=workbook.add_sheet(u'sheet_1')booksheet.col(0).width= 5120booksheet.col(1).width= 5120booksheet.col(2).width= 5120booksheet.col(3).width= 5120booksheet.col(4).width= 5120booksheet.col(5).width= 5120dom=xx.parse(r'D:\\Python27\test.xml')root = dom.documentElementrow=1col=1borders=xlwt.Borders()borders.left=1borders.right=1borders.top=1borders.bottom=1style = xlwt.easyxf('align: wrap on,vert centre, horiz center') #自动换行、水平居中、垂直居中#设置标题的格式,字体方宋、加粗、背景色:菊黄#测试项的标题title=xlwt.easyxf(u'font:name 仿宋,height 240 ,colour_index black, bold on, italic off; align: wrap on, vert centre, horiz center;pattern: pattern solid, fore_colour light_orange;')item='测试项'Subitem='测试分项'CaseTitle='测试用例标题'Condition='预置条件'actions='操作步骤'Result='预期结果'booksheet.write(0,0,item,title)booksheet.write(0,1,Subitem,title)booksheet.write(0,2,CaseTitle,title)booksheet.write(0,3,Condition,title)booksheet.write(0,4,actions,title)booksheet.write(0,5,Result,title)#冻结首行booksheet.panes_frozen=Truebooksheet.horz_split_pos= 1#一级目录for i in root.childNodes: testsuite=i.getAttribute('name').strip() #print testsuite #print testsuite ''' 写测试项 ''' print "row is :",row booksheet.write(row,col,testsuite,style) #二级目录 for dd in i.childNodes: print " %s" % dd.getAttribute('name') testsuite2=dd.getAttribute('name') if not dd.getElementsByTagName('testcase'): print "Testcase is %s" % testsuite2 row=row+1 booksheet.write(row,2,testsuite2,style) #写测试分项 row=row+1 booksheet.write(row,1,testsuite2,style) itemlist=dd.getElementsByTagName('testcase') for subb in itemlist: #print " %s" % subb.getAttribute('name') testcase=subb.getAttribute('name') row=row+1 booksheet.write(row,2,testcase,style) ilist=subb.getElementsByTagName('preconditions') for ii in ilist: preconditions=ii.firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ") col=col+1 booksheet.write(row,3,preconditions,style) steplist=subb.getElementsByTagName('actions') #print steplist for step in steplist: actions=step.firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ") col=col+1 booksheet.write(row,4,actions,style) #print "测试步骤:",steplist[0].firstChild.data.replace("<br />"," ") expectlist=subb.getElementsByTagName('expectedresults') for expect in expectlist: result=expect.childNodes[0].nodeValue.replace("<br />","" ) booksheet.write(row,5,result,style) row=row+1 workbook.save('demo.xls') |
写入excel的效果如下:

我们再来看个实例:
需要下载一个module:xlwt,如下是source code
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
import xml.dom.minidomimport xlwtimport syscol = 0row = 0def handle_xml_report(xml_report, excel): problems = xml_report.getElementsByTagName("problem") handle_problems(problems, excel) def handle_problems(problems, excel): for problem in problems: handle_problem(problem, excel)def handle_problem(problem, excel): global row global col code = problem.getElementsByTagName("code") file = problem.getElementsByTagName("file") line = problem.getElementsByTagName("line") message = problem.getElementsByTagName("message") for node in code: excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data) col = col + 1 for node in file: excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data) col = col + 1 for node in line: excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data) col = col + 1 for node in message: excel.write(row, col, node.firstChild.data) col = col + 1 row = row+1 col = 0if __name__ == '__main__': if(len(sys.argv) <= 1): print ("usage: xml2xls src_file [dst_file]") exit(0) #the 1st argument is XML report ; the 2nd is XLS report if(len(sys.argv) == 2): xls_report = sys.argv[1][:-3] + 'xls' #if there are more than 2 arguments, only the 1st & 2nd make sense else: xls_report = sys.argv[2] xmldoc = xml.dom.minidom.parse(sys.argv[1]) wb = xlwt.Workbook() ws = wb.add_sheet('MOLint') ws.write(row, col, 'Error Code') col = col + 1 ws.write(row, col, 'file') col = col + 1 ws.write(row, col, 'line') col = col + 1 ws.write(row, col, 'Description') row = row + 1 col = 0 handle_xml_report(xmldoc, ws) wb.save(xls_report) |