由于公司业务需要,花两周时间实现了一个小型的支付系统,麻雀虽小五脏俱全,各种必须的模块如账户加锁,事务性保证,流水对帐等都是有完整实现的,整个开发过程中有很多经验积累,再加上在网上搜索了一下,大部分都是些研究性的论文,对实际使用价值不大,所以这次特意拿出来和大家分享一下。
这个系统可以用作小型支付系统,也可以用做第三方应用接入开放平台时的支付流水系统。
原来的需求比较负责,我简化一点说:
对每个应用,对外需要提供 获取余额,支付设备,充值 等接口
后台有程序,每月一号进行清算
账户可以被冻结
需要记录每一次操作的流水,每天的流水都要和发起方进行对账
针对上面的需求,我们设置如下数据库:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
create table `app_margin`.`tb_status` ( `appid` int(10) unsigned not null, `freeze` int(10) not null default 0, `create_time` datetime not null, `change_time` datetime not null, primary key (`appid`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `app_margin`.`tb_account_earn` ( `appid` int(10) unsigned not null, `create_time` datetime not null, `balance` bigint(20) not null, `change_time` datetime not null, `seqid` int(10) not null default 500000000, primary key (`appid`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `app_margin`.`tb_bill` ( `id` int auto_increment not null, `bill_id` int(10) not null, `amt` bigint(20) not null, `bill_info` text, `bill_user` char(128), `bill_time` datetime not null, `bill_type` int(10) not null, `bill_channel` int(10) not null, `bill_ret` int(10) not null, `appid` int(10) unsigned not null, `old_balance` bigint(20) not null, `price_info` text, `src_ip` char(128), primary key (`id`), unique key `unique_bill` (`bill_id`,`bill_channel`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `app_margin`.`tb_assign` ( `id` int auto_increment not null, `assign_time` datetime not null, primary key (`id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `app_margin`.`tb_price` ( `name` char(128) not null, `price` int(10) not null, `info` text not null, primary key (`name`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table `app_margin`.`tb_applock` ( `appid` int(10) unsigned not null, `lock_mode` int(10) not null default 0, `change_time` datetime not null, primary key (`appid`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; insert `app_margin`.`tb_assign` (`id`,`assign_time`) values (100000000,now()); |
详细解释如下:
tb_status 应用的状态表。负责账户是否被冻结,账户的类型是什么(真实的需求是应用可能有两种账户,这里为简单所以没有列出)
appid 应用id
freeze 是否冻结
create_time 创建时间
change_time 最后一次修改时间
tb_account_earn 应用的账户余额表
appid 应用id
balance 余额(单位为分,不要用小数存储,因为小数本身不精确;另外php要在64位机下才能支持bigint)
create_time 创建时间
change_time 最后一次修改时间
seqid 操作序列号(防并发,每次update都会+1)
tb_assign 分配流水id的表,tb_bill的bill_id必须是有tb_assign分配的
id 自增id
create_time 创建时间
tb_bill 流水表。负责记录每一条操作流水,这里的bill_id不是主键,因为同一个bill_id可能会有支付和回滚两条流水
id 自增序列号
bill_id 流水号
amt 操作的金额(这个是要区别正负的,主要是为了select all的时候可以直接计算出某段时间的金额变化)
bill_info 操作的详细信息,比如3台webserver,2台db
bill_user 操作用户
bill_time 流水时间
bill_type 流水类型,区分是加钱还是减钱
bill_channel 流水来源,如充值,支付,回滚,结算还是其他
bill_ret 流水的返回码,包括未处理、成功、失败,这里的逻辑会在后面讲解
appid 应用id
old_balance 操作发生前的账户余额
price_info 记录操作发生时,记录被支付物品的单价
src_ip 客户端ip
tb_price 单价表,记录了机器的单价
name 机器唯一标识
price 价格
info 描述
tb_applock 锁定表,这是为了避免并发对某一个应用进行写操作设计的,具体的代码会在后面展示
appid 应用id
lock_mode 锁定状态。为0则为锁定,为1则为锁定
change_time 最后一次修改时间
ok,库表设计出来之后,我们就来看一下最典型的几个操作.
一. 支付操作
我这里只列出了我目前实现的方式,可能不是最好的,但应该是最经济又满足需求的。
先说调用方这里,逻辑如下:
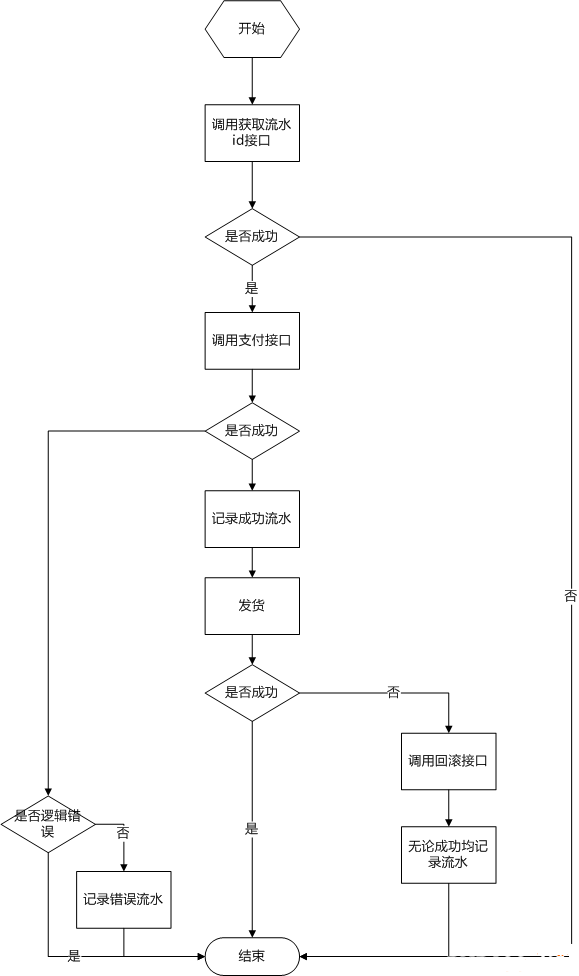
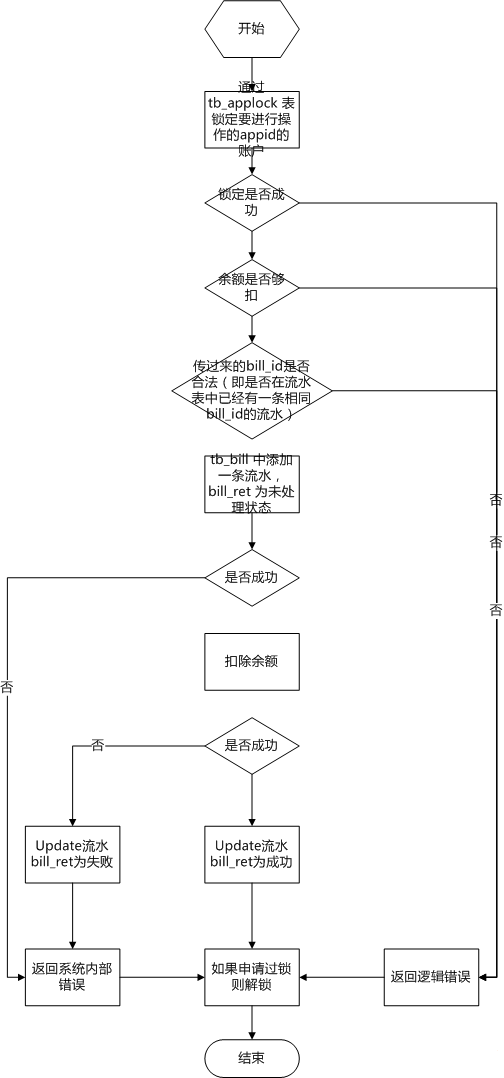
然后对应的支付系统内部逻辑如下(只列出支付操作,回滚逻辑差不多,流水检查是要检查对应的支付流水是否存在):
常用的错误返回码可能如下就足够了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
$g_site_error = array( -1 => '服务器繁忙', -2 => '数据库读取错误', -3 => '数据库写入错误', 0 => '成功', 1 => '没有数据', 2 => '没有权限', 3 => '余额不足', 4 => '账户被冻结', 5 => '账户被锁定', 6 => '参数错误', ); |
对于大于0的错误都算是逻辑错误,执行支付操作,调用方是不用记录流水的。因为账户并没有发生任何改变。
对于小于0的错误是系统内部错误,因为不知道是否发生了数据更改,所以调用方和支付系统都要记录流水。
对于等于0的返回,代表成功,两边也肯定要记录流水。
而在支付系统内部,之所以采用先写入流水,再进行账户更新的方式也是有原因的,简单来说就是尽量避免丢失流水。
最后总结一下,这种先扣钱,再发货,出问题再回滚的方式是一种模式;还有一种是先预扣,后发货,没有出问题则调用支付确认来扣款,出了问题就调用支付回滚来取消,如果预扣之后很长时间不做任何确认,那么金额会自动回滚。
二. 账户锁定的实现
这里利用了数据库的加锁机制,具体逻辑就不说了,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
|
class applock { function __construct($appid) { $this->m_appid = $appid; //初始化数据 $this->get(); } function __destruct() { $this->free(); } public function alloc() { if ($this->m_bgot == true) { return true; } $this->repairdata(); $appid = $this->m_appid; $ret = $this->update($appid,applock_mode_free,applock_mode_alloc); if ($ret === false) { app_error_log("applock alloc fail"); return false; } if ($ret <= 0) { app_error_log("applock alloc fail,affected_rows:$ret"); return false; } $this->m_bgot = true; return true; } public function free() { if ($this->m_bgot != true) { return true; } $appid = $this->m_appid; $ret = $this->update($appid,applock_mode_alloc,applock_mode_free); if ($ret === false) { app_error_log("applock free fail"); return false; } if ($ret <= 0) { app_error_log("applock free fail,affected_rows:$ret"); return false; } $this->m_bgot = false; return true; } function repairdata() { $db = app_db(); $appid = $this->m_appid; $now = time(); $need_time = $now - applock_repair_secs; $str_need_time = date("y-m-d h:i:s", $need_time); $db->where("appid",$appid); $db->where("lock_mode",applock_mode_alloc); $db->where("change_time <=",$str_need_time); $db->set("lock_mode",applock_mode_free); $db->set("change_time","now()",false); $ret = $db->update(tb_applock); if ($ret === false) { app_error_log("repair applock error,appid:$appid"); return false; } return true; } private function get() { $db = app_db(); $appid = $this->m_appid; $db->where('appid', $appid); $query = $db->get(tb_applock); if ($query === false) { app_error_log("applock get fail.appid:$appid"); return false; } if (count($query->result_array()) <= 0) { $applock_data = array( 'appid'=>$appid, 'lock_mode'=>applock_mode_free, ); $db->set('change_time','now()',false); $ret = $db->insert(tb_applock, $applock_data); if ($ret === false) { app_error_log("applock insert fail:$appid"); return false; } //重新获取数据 $db->where('appid', $appid); $query = $db->get(tb_applock); if ($query === false) { app_error_log("applock get fail.appid:$appid"); return false; } if (count($query->result_array()) <= 0) { app_error_log("applock not data,appid:$appid"); return false; } } $applock_data = $query->row_array(); return $applock_data; } private function update($appid,$old_lock_mode,$new_lock_mode) { $db = app_db(); $db->where('appid',$appid); $db->where('lock_mode',$old_lock_mode); $db->set('lock_mode',$new_lock_mode); $db->set('change_time','now()',false); $ret = $db->update(tb_applock); if ($ret === false) { app_error_log("update applock error,appid:$appid,old_lock_mode:$old_lock_mode,new_lock_mode:$new_lock_mode"); return false; } return $db->affected_rows(); } //是否获取到了锁 public $m_bgot = false; public $m_appid; } |
为了防止死锁的问题,获取锁的逻辑中加入了超时时间的判断,大家看代码应该就能看懂
三. 对帐逻辑
如果按照上面的系统来设计,那么对帐的时候,只要对一下两边成功(即bill_ret=0)的流水即可,如果完全一致那么账户应该是没有问题的,如果不一致,那就要去查问题了。
关于保证账户正确性这里,也有同事跟我说,之前在公司做的时候,是采取只要有任何写操作之前,都先取一下流水表中所有的流水记录,将amt的值累加起来,看得到的结果是否和余额相同。如果不相同应该就是出问题了。
select sum(amt) from tb_bill where appid=1;
所以这也是为什么我在流水表中,amt字段是要区分正负的原因。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。











