本文实例讲述了java使用策略模式解决商场促销商品问题。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
一 模式定义
策略模式:定义一系列的算法,将每一种算法封装起来并可以相互替换使用,策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户应用而独立变化。
二 模式举例
1 模式分析
我们借用商场促销商品来说明这一模式。

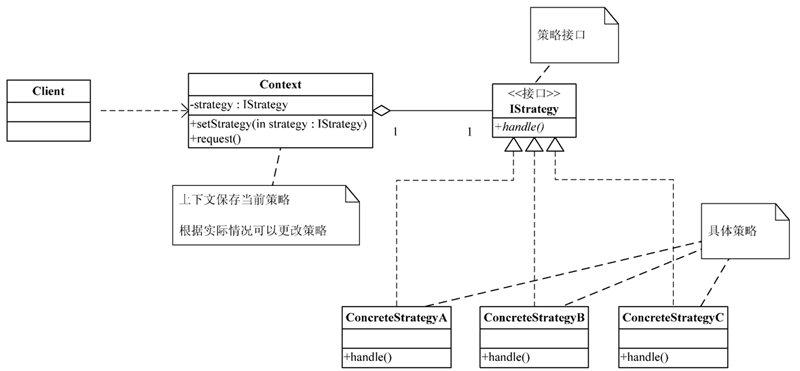
2 策略模式静态类图

3 代码示例
3.1 创建策略接口一istrategy
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package com.demo.strategy;/** * 策略接口 * * @author * */public interface istrategy { /** * 计算实际价格方法 * * @param consumeprice * 消费金额 * @return */ public double realprice(double consumeprice);} |
3.2 八折促销策略一rebatestrategy
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package com.demo.strategy;/** * 打八折商品促销策略 * * @author * */public class rebatestrategy implements istrategy { private final double rate; /** * 构造方法设置打折率 */ public rebatestrategy() { this.rate = 0.8; } /** * 计算实际价格方法 * * @param consumeprice * 消费金额 * @return */ public double realprice(double consumeprice) { return consumeprice * this.rate; }} |
3.3 满1000减200促销策略一reducestrategy
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package com.demo.strategy;/** * 满1000减200 商品促销策略 * * @author * */public class reducestrategy implements istrategy { /** * 计算实际价格方法 * * @param consumeprice * 消费金额 * @return */ public double realprice(double consumeprice) { if (consumeprice >= 1000) { return consumeprice - 200; } else { return consumeprice; } }} |
3.4 200以上部分打8折促销策略一promotionalstrategy
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package com.demo.strategy;/** * 满200,高于200部分打八折 商品促销策略 * * @author * */public class promotionalstrategy implements istrategy { /** * 计算实际价格方法 * * @param consumeprice * 消费金额 * @return */ public double realprice(double consumeprice) { if (consumeprice > 200) { return 200 + (consumeprice - 200) * 0.8; } else { return consumeprice; } }} |
3.5 创建上下文环境一context
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package com.demo.context;import java.math.bigdecimal;import com.demo.strategy.istrategy;/** * 上下文环境 * * @author * */public class context { // 当前策略 private istrategy strategy; // 设置当前策略 public void setstrategy(istrategy strategy) { this.strategy = strategy; } // 使用策略计算价格 public double cul(double consumeprice) { // 使用具体商品促销策略获得实际消费金额 double realprice = this.strategy.realprice(consumeprice); // 格式化保留小数点后1位,即:精确到角 bigdecimal bd = new bigdecimal(realprice); bd = bd.setscale(1, bigdecimal.round_down); return bd.doublevalue(); }} |
3.6 消费者购物消费一client
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
package com.demo;import java.util.random;/** * 客户端应用程序 * * @author * */public class client { /** * @param args */ public static void main(string[] args) { // 创建上下问环境对象实例 // context context = new context(); // 随机数对象 random random = new random(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 产生随机数的方式判断使用何种促销策略 int x = random.nextint(3); // 消费价格也是由随机数产生的(不能为0) double consumeprice = 0; while ((consumeprice = random.nextint(2000)) == 0) { } double realprice = consumeprice; switch (x) { case 0: // 打八折商品 // context.setstrategy(new rebatestrategy()); realprice = consumeprice * 0.8; break; case 1: // 满200,高于200部分打八折 商品 // context.setstrategy(new promotionalstrategy()); if (consumeprice > 200) { realprice = 200 + (consumeprice - 200) * 0.8; } break; case 2: // 满1000减200 商品 // context.setstrategy(new reducestrategy()); if (consumeprice >= 1000) { realprice = consumeprice - 200; } break; } system.out.print("【" + (x == 0 ? "打八折" : (x == 1 ? "高于200部分打八折" : (x == 2 ? "满1000减200" : ""))) + "】商品:"); system.out.println("原价:" + consumeprice + " - 优惠后价格:" + realprice); } }} |
4 运行结果
【满1000减200】商品:原价:908.0 - 优惠后价格:908.0
【满1000减200】商品:原价:1129.0 - 优惠后价格:929.0
【满1000减200】商品:原价:829.0 - 优惠后价格:829.0
【打八折】商品:原价:518.0 - 优惠后价格:414.40000000000003
【满1000减200】商品:原价:1230.0 - 优惠后价格:1030.0
【打八折】商品:原价:106.0 - 优惠后价格:84.80000000000001
【满1000减200】商品:原价:1134.0 - 优惠后价格:934.0
【高于200部分打八折】商品:原价:664.0 - 优惠后价格:571.2
【满1000减200】商品:原价:564.0 - 优惠后价格:564.0
【满1000减200】商品:原价:730.0 - 优惠后价格:730.0
三 该模式设计原则
1 "开-闭"原则
2 单一职责原则
四 使用场合
1 当多个类的表现行为不同,需要在运行时刻动态选择具体执行的行为的时候。
2 需要在不同情况下使用不同策略,或者策略还可能在未来用其它方式实现的时候。
3 需要隐藏具体策略的实现细节,各个具体策略彼此独立的时候。
4 当一个类中出现了多种行为,而且在一个操作中使用多个条件分支来判断使用多种行为的时候,可以使用策略模式将各个条件分支的动作植入具体策略中实现。
五 策略模式静态类图
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/chengqiuming/article/details/70139404