本文实例讲述了Java实现基于直方图应用的相似图片识别,是非常实用的技巧。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下:
一、算法概述:
首先对源图像与要筛选的图像进行直方图数据采集,对采集的各自图像直方图进行归一化再使用巴氏系数算法对直方图数据进行计算,最终得出图像相似度值,其值范围在[0, 1]之间
0表示极其不同,1表示极其相似(相同)。
二、算法步骤详解:
大致可以分为两步,根据源图像与候选图像的像素数据,生成各自直方图数据。第二步:使用第一步输出的直方图结果,运用巴氏系数(Bhattacharyya coefficient)算法,计算出相似程度值。
第一步:直方图计算
直方图分为灰度直方图与RGB直方图,对于灰度图像直方图计算十分简单,只要初始化一个大小为256的直方图数组H,然后根据像素值完成频率分布统计,假设像素值为124,则H[124] += 1, 而对于彩色RGB像素来说直方图表达有两种方式,一种是单一直方图,另外一种是三维直方图,三维直方图比较简单明了,分别对应RGB三种颜色,定义三个直方图HR,HG, HB, 假设某一个像素点P的RGB值为(4, 231,129), 则对于的直方图计算为HR[4] += 1,HG[231] += 1, HB[129] += 1, 如此对每个像素点完成统计以后,RGB彩色直方图数据就生成了。
而RGB像素的单一直方图SH表示稍微复杂点,每个颜色的值范围为0 ~ 255之间的,假设可以分为一定范围等份,当8等份时,每个等份的值范围为32, 16等份时,每个等份值范围为16,当4等份时候,每个等份值的范围为64,假设RGB值为(14, 68, 221), 16等份之后,它对应直方图索引值(index)分别为: (0, 4, 13), 根据计算索引值公式:index = R + G*16 + B*16*16
对应的直方图index = 0 + 4*16 + 13 * 16 * 16, SH[3392] += 1
如此遍历所有RGB像素值,完成直方图数据计算。
第二步:巴氏系数计算,计算公式如下:
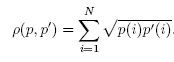
其中P, P'分别代表源与候选的图像直方图数据,对每个相同i的数据点乘积开平方以后相加
得出的结果即为图像相似度值(巴氏系数因子值),范围为0到1之间。
程序效果如下图所示:

相似度超过99%以上,极其相似
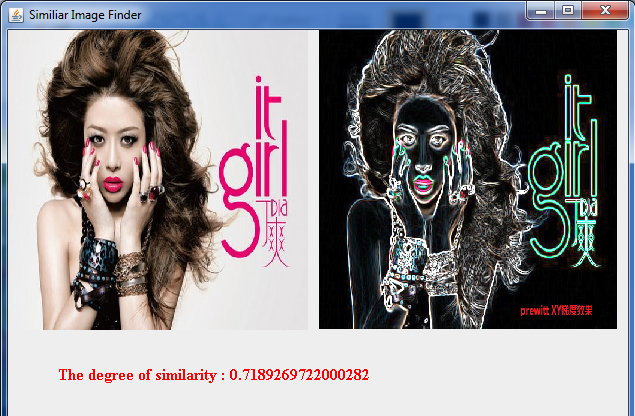
相似度为:72%, 一般相似
三、程序直方图计算源代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public void setGreenBinCount(int greenBinCount) { this.greenBins = greenBinCount; } public void setBlueBinCount(int blueBinCount) { this.blueBins = blueBinCount; } public float[] filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) { int width = src.getWidth(); int height = src.getHeight(); int[] inPixels = new int[width*height]; float[] histogramData = new float[redBins * greenBins * blueBins]; getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels ); int index = 0; int redIdx = 0, greenIdx = 0, blueIdx = 0; int singleIndex = 0; float total = 0; for(int row=0; row<height; row++) { int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0; for(int col=0; col<width; col++) { index = row * width + col; ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff; tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff; tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff; tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff; redIdx = (int)getBinIndex(redBins, tr, 255); greenIdx = (int)getBinIndex(greenBins, tg, 255); blueIdx = (int)getBinIndex(blueBins, tb, 255); singleIndex = redIdx + greenIdx * redBins + blueIdx * redBins * greenBins; histogramData[singleIndex] += 1; total += 1; } } // start to normalize the histogram data for (int i = 0; i < histogramData.length; i++) { histogramData[i] = histogramData[i] / total; } return histogramData; } |
计算巴氏系数的代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/** * Bhattacharyya Coefficient * http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~kosta/CompVis_Notes/bhattacharyya.pdf * * @return */public double modelMatch() { HistogramFilter hfilter = new HistogramFilter(); float[] sourceData = hfilter.filter(sourceImage, null); float[] candidateData = hfilter.filter(candidateImage, null); double[] mixedData = new double[sourceData.length]; for(int i=0; i<sourceData.length; i++ ) { mixedData[i] = Math.sqrt(sourceData[i] * candidateData[i]); } // The values of Bhattacharyya Coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, double similarity = 0; for(int i=0; i<mixedData.length; i++ ) { similarity += mixedData[i]; } // The degree of similarity return similarity; } |
希望本文所述对大家的Java程序设计有所帮助。











